# 基本概念
数据结构是计算机的基础,算法是计算机科学
常听到算法的时候,就会有人说到时间复杂度,空间复杂度。那么这两个是什么意思呢?

# 时间复杂度
其实就是一个函数,用大O表示,比如O(1)、O(n)...
它的作用就是用来定义没描述算法的运行时间
O(1)
let i = 0; i += 1;O(n): 如果是O(1) + O(n)则还是O(n)
for(let i = 0; i < n; i++) { console.log(i) }O(n^2): O(n) * O(n^2),也就是双层循环,自此类推:O(n ^ 3)
for (let i = 0; i < n; i += 1) { for(let j = 0; j < n; j += 1) { console.log(i, j) } }O(logn): 就是求log以2为底的多少次方等于n
// 例:2^3 =8 // 那么 log(2) 8 = 3 // 这个例子就是求2的多少次方会大于n,然后就会结束循环。这就是一个典型的O(logn); let i = 1; while(i < n) { console.log(i); i *= 2; }
# 空间复杂度
和时间复杂度一样,空间复杂度也是用大O表示,比如O(1)、O(n)...
它用来定义描述算法运行过程中临时占用的存储空间大小
占用越少,代码写的就越好
O(1):单个变量,所以占用永远是O(1)
let i = 0; i += 1;O(n): 声明一个数组,添加n个值,相当于占用了n个空间单元
const arr = []; for(let i = 0; i < n; i += 1) { arr.push(i); }O(n ^ 2):类似一个矩阵的概念,就是二维数组的意思
const arr = []; for(let i = 0; i < n; i += 1) { arr.push([]); for(let j = 0; j < n; j += 1) { arr[i].push(j); } }
# 数据结构
# 1.栈
一个先进后出的数据结构
按照常识理解就是有序的挤公交,最后上车的人会在门口,然后门口的人会最先下车
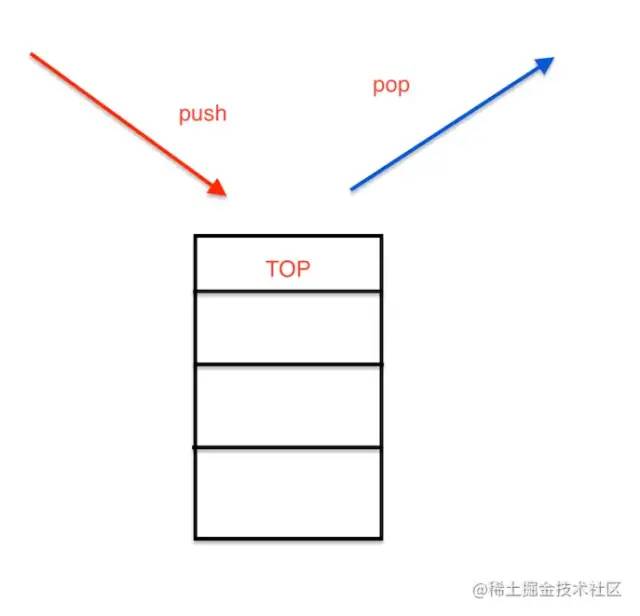
js中没有栈的数据类型,但我么可以通过Array来模拟一个
const stack = [];
stack.push(1); // 入栈
stack.push(2); // 入栈
const item1 = stack.pop(); // 出栈元素
十进制转二进制
// 时间复杂度O(n) n为二进制的长度 // 空间复杂度O(n) n为二进制长度 const dec2bin = dec => { // 创建一个字符串 let res = ''; // 创建一个栈 let stack = []; // 遍历数字 如果大于0 就可以继续转换2进制 while(dec > 0) { // 将数字的余数入栈 stack.push(dec % 2); // 除以2 dec = dec >> 1; } // 取出栈中的数字 while(stack.length) { res += stack.pop(); } // 返回这个字符串 return res; }判断字符串的有效符号
// 时间复杂度O(n) n为s的length // 空间复杂度O(n) const isValid = s => { // 如果长度不等于2的倍数肯定不是一个有效的括号 if(s.length % 2 === 1) return false; // 创建一个栈 let stack = []; // 遍历字符串 for(let i = 0; i < s.length; i++) { const c = s[i]; // 如果是左括号就入栈 if(c === '(' || c === '{' || c === '[') { stack.push(c); } else { // 如果不是左括号,且栈为空 肯定不是一个有效括号 返回false if(!stack.length) return false; // 拿到最后一个左括号 const top = stack[stack.length - 1]; // 如果是右括号和左括号能匹配就出栈 if((top === '(' && c === ')') || (top === '{' && c === '}') || (top === '[' && c === ']')) { stack.pop(); } else { // 否则就不是一个有效的括号 return false; } } } return stack.length === 0; }
# 2.队列
和栈相反先进先出的一个数据结构
按照尝试理解就是银行排号办理业务,先去领号排队的人,先办理业务
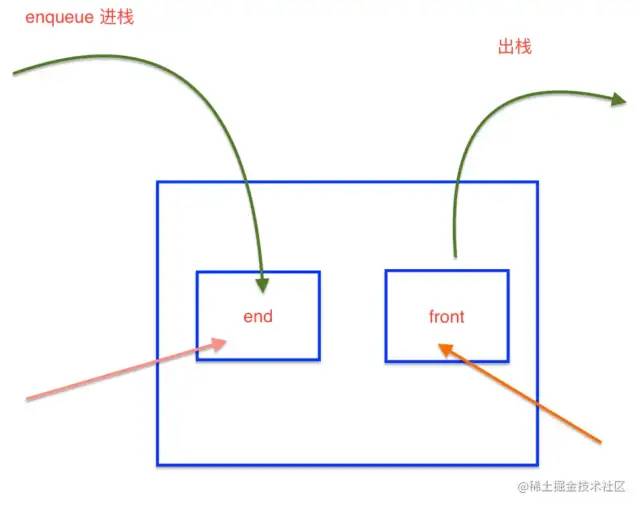
同样js中没有栈的数据类型,但同样可以通过Array来模拟一个
const queue = [];
// 入队
queue.push(1);
queue.push(2);
// 出队
const first = queue.shift();
const end = queue.shift();
最近的请求次数
const RecentCounter = function() { // 初始化队列 this.q = []; } // 输入 inputs = [[],[1],[100],[3001],[3002]] 请求间隔为 3000ms // 输出 outputs = [null,1,2,3,3] // 时间复杂度 O(n) n为剔出老请求的长度 // 空间复杂度 O(n) n为最近请求的次数 RecentCounter.prototype.ping = function(t) { // 如果传入的时间小宇等于最近请求的时间,则直接返回0 if(!t) return null; // 将传入的时间放入队列 this.q.push(t); // 如果队头小于t - 3000 则剔除对垒 while(this.q[0] < t - 3000) { this.q.shift(); } // 返回最近的请求次数 return this.q.length; }滑动窗口最大值
// 给你一个整数数组 nums,有一个大小为 k 的滑动窗口从数组的最左侧移动到数组的最右侧。你只可以看到在滑动窗口内的 k 个数字。滑动窗口每次只向右移动一位。 // 返回 滑动窗口中的最大值 。 // 输入:nums = [1,3,-1,-3,5,3,6,7], k = 3 // 输出:[3,3,5,5,6,7] // 解释: // 滑动窗口的位置 最大值 // --------------- ----- // [1 3 -1] -3 5 3 6 7 3 // 1 [3 -1 -3] 5 3 6 7 3 // 1 3 [-1 -3 5] 3 6 7 5 // 1 3 -1 [-3 5 3] 6 7 5 // 1 3 -1 -3 [5 3 6] 7 6 // 1 3 -1 -3 5 [3 6 7] 7 const maxSlidingWindow = (nums,k) => { // const n = nums.length; // const q = []; // for (let i = 0; i < k; i++) { // while (q.length && nums[i] >= nums[q[q.length - 1]]) { // q.pop(); // } // q.push(i); // } // const ans = [nums[q[0]]]; // for (let i = k; i < n; i++) { // while (q.length && nums[i] >= nums[q[q.length - 1]]) { // q.pop(); // } // q.push(i); // while (q[0] <= i - k) { // q.shift(); // } // ans.push(nums[q[0]]); // } // return ans; let queue = [], result = []; for(let i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) { // 如果队列不为空,且要入队的元素大于队尾元素,队尾元素出队 ---这种方式替代Math.max.apply(null, arr) while(queue.length > 0 && nums[i] > nums[queue[queue.length - 1]]) { queue.pop(); } queue.push(i); // j是把i作为滑动窗口最后一个值时滑动窗口第一个值的索引 const j = i - k + 1; // j >= 0 说明滑动窗口已构建完毕 if(j >= 0) { // 当队首元素不属于当前滑动窗口时出队 if(queue[0] < j) queue.shift(); result.push(nums[queue[0]]); } } return result; }
# 3.链表
多个元素组成的列表,元素存储不连续,通过next指针来链接,最底层为null
就类似于父辈链接关系吧,比如:你爷爷的儿子是你爸爸,你爸爸的儿子是你,而你假如目前还没有结婚生子,那你就暂时木有儿子
js中类似于链表的典型就是原型链,但是js中没有链表这种数据结构,我们可以通过一个object来模拟链表
const a = {
val: 'a'
}
const b = {
val: 'b'
}
const c = {
val: 'c'
}
const d = {
val: 'd'
}
a.next = b;
b.next = c;
c.next = d;
// 得到
const linkList = {
val: 'a',
next: {
val: 'b',
next: {
val: 'c',
next: {
val: 'd',
next = null
}
}
}
}
// 遍历链表
let p = a;
while(p) {
console.log(a.val);
p = p.next;
}
// 插入
const e = {val: 'e'};
c.next = e;
e.next = d;
// 删除
c.next = d;
手写instaceOf
const myInstanceof = (A, B) => { // 声明一个指针 let p = A; // 遍历这个链表 while(p) { if(p === B.prototype) return false; p = p.__proto__; } return false; } myInstanceof([], Object.assign)删除链表中的节点
// 时间复杂和空间复杂度都是O(1) const deleteNode = node => { // 把当前链表的指针指向下一个链表的值就可以了 node.val = node.next.val; node.next = node.next.next; }删除链表中的重复元素
// 1 -> 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 3 // 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> null // 时间复杂度 O(n) n为链表的长度 // 空间复杂度 O(1) const deleteDuplicates = head => { let p = head; while(p && p.next) { if(p.val === p.next.val) { p.next = p.next.next; } else { p = p.next; } } return head; }反转链表
// 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 -> null // 5 -> 4 -> 3 -> 2 -> 1 -> null // 时间复杂度O(n) n为链表的长度 // 空间复杂度O(1); const reverseList = head => { // 创建一个指针 let p1 = head; // 创建一个新指针 let p2 = null; // 遍历链表 while(p1) { // 创建一个临时遍历 let temp = p1.next; // 将当前节点的下一个节点指向新链表 p1.next = p2; // 将新链表指向当前节点 p2 = p1; // 将当前节点指向临时遍历 p1 = tem; } // 最后返回新的这个链表 return p2; }
# 4.集合
一种无序且唯一的数据结构
ES6中有集合Set类型
const arr = [1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 3];
// 去重
const arr2 = [...new Set(arr)];
// 判断元素是否在集合中
const set = new Set(arr);
set.has(2) // true
// 交集
const set2 = new Set([1, 2]);
const set3 = new Set([...set].filter(item => set.has(item)));
去重
两个数组的交集
// 时间复杂度 O(n^2) n为数组长度 // 空间复杂度 O(n) n为去重后的数组长度 const intersection = (nums1, nums2) => { // 通过数组的filter选出交集 // 然后通过 Set集合 去重 并生成数组 return [...new Set(nums1.filter(item => nums2.includes(item)))]; }
# 5. 字典
与集合类似,一个存储唯一值的结构,以键值对的形式存储
js中有字典数据结构,就是Map类型
两数之和
// nums = [2, 7, 11, 15] target = 9 // 时间复杂度O(n) n为nums的length // 空间复杂度O(n) const twoSum = function(nums, target) { // 建立一个字典数据结构来保存需要的值 const map = new Map(); for(let i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) { // 获取当前的值,和需要的值 let n = nums[i]; let n2 = target - n; // 如果字典中有需要的值,则匹配成功 if(map.has(n2)) { return [map.get(n), i]; } else { map.set(n, i); } } }两个数组的交集
// nums1 = [1,2,2,1], nums2 = [2,2]; //输出[2]; // 时间复杂度 O(m + n) m为nums1长度, n 为nums2的长度 // 空间复杂度O(m) m为交集的数组长度 const intersection = (nums1, nums2) => { let map = new Map(); nums1.forEach(n => map.set(n, true)); // 创建一个新数组 let res = []; nums2.forEach(n => { if(map.has(n)) { res.push(n); map.delete(n); } }) return res; }字符的有效的括号
// 用字典优化 // 时间复杂度O(n) n为s的字符长度 // 空间复杂度 O(n) const isValid = s => { // 如果长度不等于2的倍数肯定不是一个有效的括号 if(s.length % 2 !=== 0) return false; // 创建一个字典 const map = new Map(); map.set('(', ')'); map.set('[', ']'); map.set('{', '}'); // 创建一个栈 const stack = []; // 遍历字符串 for(let i = 0; i < s.length; i++) { // 取出字符 const c = s[i]; // 如果是左括号就入栈 if(map.has(c)) { stack.push(c); } else { // 取出栈顶 const t = stack[stack.length - 1]; // 如果字典中有这个值 就出栈 if(map.get(t) === c) { stack.pop(); } else { return false; } } } return stack.length === 0; }最小覆盖子串
// 输入:s = "ADOBECODEBANC", t = "ABC" // 输出:"BANC" // 时间复杂度 O(m + n) m是t的长度 n是s的长度 // 空间复杂度 O(k) k是字符串中不重复字符的个数 const minWindow = (s, t) => { // 定义双指针维护一个滑动窗口 let l = 0; let r = 0; // 建立一个字典 const need = new Map(); // 遍历t for (const c of t) { need.set(c, need.has(c) ? need.get(c) + 1 : 1) } let needType = need.size; // 记录最小子串 let res = '' // 移动右指针 while(r < s.length) { // 获取当前字符 const c = s[r]; // 如果字典里有这个字符 if(need.has(c)) { // 减少字典里面的次数 need.set(c, need.get(c) - 1); // 减少需要的值 if(need.get(c) === 0) needType -= 1; } // 如果字典里所有所有的值都为0了,就说明找到了一个最小子串 while(needType === 0) { // 取出当前符合的子串 const newRes = s.substring(l, r + 1); // 如果当前子串是小于上次的子串就进行覆盖 if(!res || newRes.length < res.length) res = newRes; // 获取左指针的字符 const c2 = s[l]; // 如果字典里有这个字符 if(need.has(c2)) { // 增加字典里的次数 need.set(c2, need.get(c2) + 1); // 增加需要的值 if(need.get(c2) === 1) needType += 1; } l += 1; } r += 1; } return res; }
# 5. 树
一种分层数据的抽象模型,比如DOM树、树形控件
js中没有树,但是可以用Object和Array构件数
# 普通树
```js
// 这就是一个常见的普通树形结构
const tree = {
val: "a",
children: [
{
val: "b",
children: [
{
val: "d",
children: [],
},
{
val: "e",
children: [],
}
],
},
{
val: "c",
children: [
{
val: "f",
children: [],
},
{
val: "g",
children: [],
}
],
}
],
}
```
深度优先遍历
- 尽可能深的搜索树的分支,就比如遇到一个节点就会直接去遍历他的子节点,不会立刻去遍历他的兄弟节点
- 口诀:访问根节点,对根节点的childrend挨个进行深度优先遍历
// 深度优先遍历 const dfs = tree => { tree.children.forEach(dfs); }广度优先遍历
- 先访问离根节点最近的节点, 如果有兄弟节点就会先遍历兄弟节点,再去遍历自己的子节点
- 口诀:新建一个队列 并把根节点入队;把对头出队并访问;把队头的childrend挨个入队;重复第二、三步,直到队列为空
// 广度优先遍历 const bfs = tree => { const q = [tree]; while(q.length) { const n = q.shift(); console.log(n.val); n.children.forEach(c => q.push(c)) } }
# 二叉树
树中每个节点 最多只能有两个子节点
const bt = {
val: 1,
left: {
val: 2,
left: null,
right: null;
},
right: {
val: 3,
left: {
val: 4,
left: null,
right: null
},
right: {
val: 5,
left: null,
right: null
}
}
}
二叉树的先序遍历
// 先序遍历,递归 const preOrder = tree => { if(!tree) return; console.log(tree.val); preOrder(tree.left); preOrder(tree.right); } // 非递归 循环的形式 const preOrder2 = tree => { if(!tree) return; const stack = [tree]; while(stack.length) { const n = stack.pop(); console.log(n.val); if(n.right) stack.push(n.right); if(n.left) stack.push(n.left); } }二叉树的中序遍历
// 中序遍历 递归 const inOrder = tree => { if(!tree) return; inorder(tree.left); console.log(tree.val); inorder(tree.right); } // 循环形式 const inorder2 = tree => { if(!tree) return; const stack = []; // 先遍历所有的左节点 let p = tree; while(stack.length || p) { while(p) { stack.push(p); p = p.left; } const n = stack.pop(); console.log(n.val); p = n.right; } }二叉树的后序遍历
// 后序遍历 递归 const postOrder = tree => { if(!tree) return; postOrder(tree.left) postOrder(tree.right) console.log(tree.val) } // 循环 const postOrder2 = tree => { if(!tree) return; const stack = [tree]; const outputStack = []; while(stack.length) { const n = stack.pop(); outputStack.push(n) if(n.left) stack.push(n.left); if(n.right) stack.push(n.right); } while(outputStack.length) { const n = outputStack.pop(); console.log(n.val) } }二叉树的最大深度
// 给一个二叉树,需要你找出其最大的深度,从根节点到叶子节点的距离 // 时间复杂度 O(n) n为树的节点数 // 空间复杂度 有一个递归调用的栈 所以为 O(n) n也是为二叉树的最大深度 const maxDepth = function(root) { let res = 0; const dfs = (n, l) => { if(!n) return; if(!n.left && !n.right) { // 没有叶子节点就把深度数量更新 res = Math.max(res, l); } dfs(n.left, l + 1); dfs(n.right, l + 1) } dfs(root, 1) return res; }二叉树的最小深度
// 给一个二叉树,需要你找出其最小的深度, 从根节点到叶子节点的距离 // 时间复杂度O(n) n是树的节点数量 // 空间复杂度O(n) n是树的节点数量 const minDepth = root => { if(!root) return 0; let stack = [[root, 1]]; while(stack.length) { const [n, l] = stack.shift(); if(!n.left && !n.right) return l; n.left && stack.push([n.left, l + 1]); n.right && stack.push([n.right, l + 1]); } }
# 7.图
图是网络结构的抽象模型,是一组由边连接的节点
js中可以利用Object和Array构建图
// 上图可以表示为
const graph = {
0: [1, 2],
1: [2],
2: [0, 3],
3: [3]
}
// 深度优先遍历,对根节点没有访问过的相邻节点挨个进行遍历
{
// 记录节点是否访问过
const visited = new Set();
const dfs = n => {
visited.add(n);
// 遍历相邻节点
graph[n].forEach(c => {
// 没访问过才可以,进行递归访问
if(!visited.has(c)) {
dfs(c)
}
})
}
// 从2开始进行遍历
dfs(2)
}
// 从广度优先遍历
{
const visited = new Set();
// 新建一个队列,根节点入队,设2为根节点
const q = [2];
visited.add(2);
while(q.length) {
// 对头出队,并访问
const n = q.shift();
console.log(n);
graph[n].forEach(c => {
// 对没访问过的相邻节点入队
if(!visited.has(c)) {
q.push(c);
visited.add(c);
}
})
}
}
有效数字-
// 生成数字关系图 只有状态为 3 5 6 的时候才为一个数字 const graph = { 0: { 'blank': 0, 'sign': 1, ".": 2, "digit": 6 }, 1: { "digit": 6, ".": 2 }, 2: { "digit": 3 }, 3: { "digit": 3, "e": 4 }, 4: { "digit": 5, "sign": 7 }, 5: { "digit": 5 }, 6: { "digit": 6, ".": 3, "e": 4 }, 7: { "digit": 5 }, } // 时间复杂度 O(n) n是字符串长度 // 空间复杂度 O(1) const isNumber = s => { // 记录状态 let state = 0; // 遍历字符串 for(c of s.strim()) { // 把字符进行转换 if(c >= '0' && c <= '9') { c = 'digit'; } else if(c === ' ') { c = 'blank'; } else if(c === '+' || c === '-') { c = 'sign'; } else if(c === 'E' || c === 'e') { c = 'e'; } // 开始寻找图 state = graph[state][c]; // 如果最后是undefined就是错误 if(state === 'undefined')return false; } // 判断最后的结果是不是合法的数字 if(state === 3 || state === 5 || state == 6) return true; return false; }
# 8.堆--重要
一种特殊的完全二叉树,所有的节点都大于等于最大堆,或者小于等于最小堆的子节点
js通常使用数组来表示堆
- 左侧子节点的位置是2*index + 1
- 右侧子节点的位置是2 * index + 2
- 父节点的位置是(index - 1) / 2,取余数
大顶堆举例
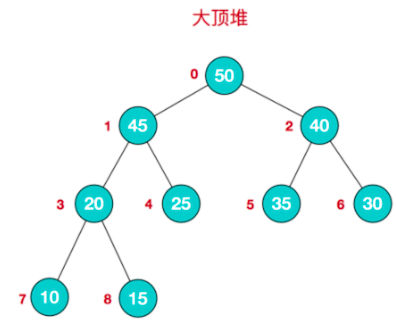
对堆中的节点按层进行编号,映射到数组中如下图
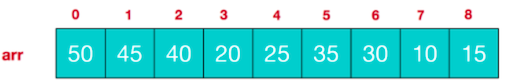
大顶堆的特点:arr[i] >= arr[2 * i + 1] && arr[i] >= arr[2 * i + 2], i 对应第几个节点,i 从0开始编号
小顶堆举例
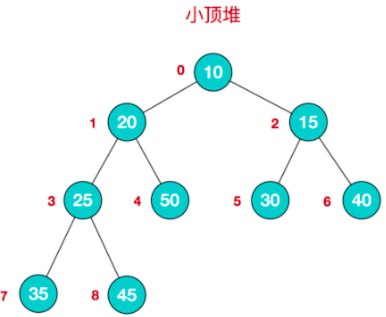
小顶堆特点:arr[i] <= arr[i * i + 1] && arr[i] <= arr[2 * i + 2].i对应第几个节点,i从0开始
React任务调度背后的算法 - LeetCode 703. 数据流中的第 K 大元素 (opens new window)
# JS实现一个最小堆
class MinHeap {
constructor() {
// 元素容器
this.heap = [];
}
// 交换节点的值
swap(i1, i2) {
[this.heap[i1], this.heap[i2]] = [this.heap[i2], this.heap[i1]];
}
// 获取父节点
getParentIndex(index) {
// 除以二,取余数
return (index - 1) >> 1;
}
// 获取左侧节点索引
getLeftIndex(i) {
return (i << 1) + 1
}
// 获取右侧节点索引
getRightIndex(i) {
return (i << 1) + 2;
}
// 上移
shiftUp(index) {
if(index === 0) return;
// 获取父节点
const parentIndex = this.getParentIndex(index);
// 如果父节点的值大于当前节点的值,就需要进行交换
if(this.heap[parentIndex] > this.heap[index]) { // 如果是大顶堆 this.heap[parentIndex] < this.heap[index]
this.swap(parentIndex, index);
//然后继续上移
this.shiftUp(parentIndex);
}
}
// 下移
shiftDown(index) {
// 获取左右节点索引
const leftIndex = this.getLeftIndex(index);
const rightIndex = this.getRightIndex(index);
// 如果左子节点小于当前的值
if(this.heap[leftIndex] < this.heap[index]) { // 如果是大顶堆 this.heap[leftIndex] > this.heap[index]
// 进行节点交换
this.swap(leftIndex, index);
// 继续进行下移
this.shiftDown(leftIndex)
}
// 如果右侧节点小于当前值
if(this.heap[rightIndex] < this.heap[index]) { // 如果是大顶堆 this.heap[rightIndex] < this.heap[index]
this.swap(rightIndex, index);
this.shiftDown(rightIndex)
}
}
// 插入元素
insert(value) {
// 插入到堆的底部
this.heap.push(value);
// 然后上移:将这个值和它的父节点进行交换,直到父节点小宇等于这个插入的值
this.shiftUp(this.heap.length - 1);
}
// 删除堆顶
pop() {
// 把数组最后以为,转移到数组头部
this.heap[0] = this.heap.pop();
// 进行下移操作
this.shiftDown(0)
}
// 获取堆顶元素
peek() {
return this.heap[0]
}
// 获取堆大小
size() {
return this.heap.length;
}
}
# 数组中的第k个最大元素
// 输入 [3,2,1,5,6,4] 和 k = 2
// 输出 5
// 时间复杂度 O(n * logK) K就是堆的大小
// 空间复杂度 O(K) K是参数k
const findKthLargest = function(nums, k) {
// 使用上面js实现的最小堆,来构建一个最小堆
const h = new MinHeap();
// 遍历数组
nums.forEach(n => {
// 把数组中的值依次插入到堆里
h.insert(n);
if(h.size() > k) {
// 进行优胜劣汰
h.pop();
}
})
return h.peek();
}
# 前K个高频元素
// nums = [1,1,1,2,2,3], k = 2;
// 输出[1,2]
// 时间复杂度 O(n * logK)
// 空间复杂度 O(k)
const topKFrequent = function(nums, k) {
// 统计每个元素出现的频率
const map = new Map();
// 遍历数组,简历映射关系
num.forFach(n => {
map.set(n, map.has(n) ? map.get(n) + 1 : 1);
})
// 简历最小堆
const h = new MinHeap();
// 遍历映射关系
map.forEach((value, key) => {
// 由于插入的元素结构发生了变化,所以需要对 最小堆的类 进行改造一下,改造方法我会写到最后
h.insert({value, key})
if(h.size() > k) {
h.pop();
}
})
return h.heap.map(item => item.key)
}
// 改造上移和下移操作即可
// shiftUp(index) {
// if (index == 0) return;
// const parentIndex = this.getParentIndex(index);
// if (this.heap[parentIndex] && this.heap[parentIndex].value > this.heap[index].value) {
// this.swap(parentIndex, index);
// this.shiftUp(parentIndex);
// }
// }
// shiftDown(index) {
// const leftIndex = this.getLeftIndex(index);
// const rightIndex = this.getRightIndex(index);
// if (this.heap[leftIndex] && this.heap[leftIndex].value < this.heap[index].value) {
// this.swap(leftIndex, index);
// this.shiftDown(leftIndex)
// }
// if (this.heap[rightIndex] && this.heap[rightIndex].value < this.heap[index].value) {
// this.swap(rightIndex, index);
// this.shiftDown(rightIndex)
// }
// }
# 常见算法及算法思想
把某个乱序的数组编程升序或者降序的数组,js比较常用sort方法进行排序
# 排序
# 1.冒泡排序
- 比较所有相邻元素,如果第一个比第二个大就交换他们
- 执行一次后可以保证最后一个数字是最大的
- 重新执行n - 1次,就可以完成排序
// 时间复杂度 O(n ^ 2) n为数组长度
// 空间复杂度O(1)
Array.prototype.bubbleSort = function() {
for(let i = 0; i < this.length; i++) {
for(let j = 0; j < this.length; j++) {
if(this[j] > this[j + 1]) {
// 交换数据
[this[j], this[j + 1]] = [this[j + 1], this[j]];
}
}
}
}
# 2.选择排序
- 找到数组中最小的值,选中它并排到第一位
- 接着找到数组中第二小的值,选中它并放到第二位
- 重复上述步骤执行n- 1次
// 时间复杂度O(n ^2) n为数组长度
// 空间复杂度 O(1)
Array.prototype.selectionSort = function() {
for(let i = 0; ii < this.length - 1; i++) {
let indexMin = i;
for(let j = i; j < this.length;j++) {
// 如果当前这个元素 小宇最小值的下标 就更新最小值的小标
if(this[j] < this[indexMin])) {
indexMin = j;
}
}
// 避免自己和自己进行交换
if(indexMin !== i) {
// 进行交换数据
[this[i], this[indexMin]] = [this[indexMin], this[i]]
}
}
}
# 3.插入排序
- 从第二个数,开始往前比较
- 如它大就往后排
- 以此类推进行到最后一个数
// 时间复杂度 O(n ^ 2)
Array.prototype.insertionSort = function() {
// 遍历数组 从第二个开始
for(let i = 1; i< this.length; i++) {
// 获取第二个元素
const temp = this[i];
let j = i;
while(j > 0) {
// 如果当前元素小于前一个元素 就开始往后移动
if(this[j - 1] > temp) {
this[j] = this[j - 1];
} else {
// 否则就跳出循环
break;
}
j--;
}
// 前一位置赋值给当前元素
this[j] = temp;
}
}
# 3.归并排序
- 分:把数组劈成两半 在递归的对子数组进行分操作,直到分成一个个单独的数
- 合:把两个数合并为有序数组,在对有序数组进行合并,直到全部子数组合并成一个完整的数组
// 时间复杂度O(nlogn) 分需要劈开数组,所以是logn,合则是n
// 空间复杂度O(n)
Array.prototype.mergeSort = function() {
const rec = arr => {
// 递归终点
if(arr.length === 1) return arr;
// 获取中间索引
const mid = arr.length >> 1;
// 通过中间下标,进行分割数组
const left = arr.slice(0, mid);
const right = arr.slice(mid);
// 左边和右边的数组进行递归,会得到有序的左数组,和有序的右数组
const orderLeft = rec(left);
const orderRight = rec(right);
// 存放结果的数组
const res = [];
while(orderLeft.length || orderRight.length) {
// 如左边和右边数组都有值
if(orderLeft.length && orderRight.length) {
// 左边对头的值小于右边对头的值, 就左边对头出对,否则就是右边对头出对
res.push(orderLeft[0] < orderRight[0] ? orderLeft.shift() : orderRight.shift())
} else if(orderLeft.length) {
// 把左边的对头放入数组
res.push(orderLeft.shift());
} else if(orderRight.length) {
// 把右边的对头放入数组
res.push(orderRight.shift())
}
}
return res;
}
const res = rec(this);
// 把结果放入袁术
res.forEach((n, i) => this[i] = n)
}
- 合并两个有序链表
// 时间复杂度O(n) n为链表1和链表2的长度之和 // 空间复杂度O(1) const mergeTwoLists = function(list1, list2) { // 新建一个新链表 作为返回值 const res = { val: 0, next: null } // 指向新链表的指针 let p = res; // 新疆两个指针 let p1 = list1 let p2 = list2; // 遍历两个链表 while(p1 && p2) { // 如果链表1 小于 链表2的值 就接入链表1的值 if(p1.val < p2.val) { p.next = p1; p1 = p1.next; } else { p.next = p2; p2 = p2.next; } p = p.next; } // 如果链表1或者链表2还有值,就把后面的值全部接入新链表 if(p1) { p1.next = p1; } if(p2) { p.next = p2; } return res.next; }
# 5.快速排序
- 分区: 从数组中任意选择一个基准,所有比基准小的元素都放在基准前面,比基准大的元素放在基准后面
- 递归: 递归的对基准前后的子元素进行分区
// 时间复杂度O(nlongN);
// 空间复杂度O(1)
Array.prototype.quickSort = function() {
const rec = arr => {
// 如果数组长度小于等于1 就不用排序了
if(arr.length <= 1) return arr;
// 存放基准前后的数组
const left = [];
const right = [];
// 取基准
const mid = arr[0];
for(let i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
// 如果当前值小于基准就放到基准前数组里面
if(arr[i] < mid) {
left.push(arr[i]);
} else {
// 否则就放到基准后数组里面
right.push(arr[i])
}
}
// 递归调用两边的子数组
return [...rec(left), mid, ...rec(right)]
}
const res = rec(this);
res.forEach((n, i) => this[i] = n)
}
# 搜索
找出数组中某个元素的下标,js中通常使用indexOf方法进行搜索
# 顺序搜索
- 就比如indexOf方法,从头开头搜索数组中的某个方法
# 二分搜索
- 从数组中的中间位置开始搜索,如果中间元素正好是目标值,则搜索结束
- 如果目标值大于或小于中间元素,则大于或小于中间元素的那一半数组中搜索
- 数组必须是有序的,如不是则需要先进行排序
```js
// 时间复杂度O(log n)
// 空间复杂度O(1)
Array.prototype.binarySearch = function(target) {
// 代表数组的最小索引
let low = 0;
// 和最大索引
let higt = this.length - 1;
while(low <= higt) {
// 获取中间元素索引
const mid = (low + high) >> 1;
const element = this[mid];
// 如果中间元素小于要查找的元素, 就把最小索引更新为中间索引的下一个
if(element < target) {
low = mid + 1;
} else if(element > target) {
// 如果中间元素大于要查找的元素,就把最大索引更新为中间索引的额前一个
higt = mid - 1;
} else {
return mid;
}
}
return -1;
}
```
猜数字大小
// 时间复杂度O(logn) 分割成两半的 基本都是logn // 空间复杂度O(1) const guessNumber = n => { // 定义范围最大值和最小值 const low = 1; const high = n; while(low <= high) { // 获取中间值 const mid = (low + high) >>> 1; // 这个方法是leetcode中方法 // 如果返回值为-1,就是小了 // 如果返回值为1 就是大了 // 如果返回值为0 就是找到了 const res = guess(mid); // 剩下的操作就和二分搜索一样了 if(res === 0) { return mid; } else if(res === 1) { low = mid + 1; } else { high = mid - 1; } } }
# 分而治之
算法设计中的一种思想,将一个问题分成多个子问题,递归解决子问题,然后将子问题的解合并成最终的解
- 归并排序
- 分:把数组从中间一分为二
- 解:递归的对两个子数组进行递归排序
- 合:合并有序子数组
- 快速排序
- 分:选基准,按基准吧数组分成两个子数组
- 解: 递归对两个子数组进行快速排序
- 合: 对两个子数组进行合并
- 二分搜索
- 二分搜索也属于分而治之的思想
分而治之思想:猜数字大小
// 时间复杂度O(logn) // 空间复杂度O(logn) 递归调用栈 所以是logn const guessNumber = n => { // 递归函数,接受一个搜索范围 const rec = (low, high) => { // 递归结束条件 if(low > high) return; // 获取中间元素 const mid = (low + high) >> 1; // 这个方法是 leetcode 中的方法 // 如果返回值为-1 就是小了 // 如果返回值为1 就是大了 // 如果返回值为0 就是找到了 const res = guess(mid); // 猜对 if(res === 0) { returm mid; } else if(res === 1) { // 猜大了 return rec(mid + 1, high) } else { // 猜小了 return rec(low, mid - 1) } } return rec(1, n); }分而治之思想:翻转二叉树
// 时间复杂度O(n) n为树的节点数量 // 空间复杂度O(n) h为树的高度 const invertTree = root => { if(!root) return null; return { val: root.val, left: invertTree(root.right), right: invertTree(root.left) } }分而治之思想:相同的树
// 时间复杂度 o(n) n为树的节点数量 // 空间复杂度 o(h) h为树的节点数 const isSameTree = (p, q) => { if(!p && !q) return true; if(p && q && p.val === q.val && isSameTree(p.left, q.left) && isSameTree(p.right, q.right)) { return true; } return false; }分而治之思想:对称二叉树
// 时间复杂度 O(n) // 空间复杂度 O(n) const isSymmetric = root => { if(!root) return true; const isMirror = (l, r) => { if(!l && !r) return true; if(l && r && l.val === r.val && isMirror(l.left, r.right) && isMirror(l.right, r.right)) { return true; } return false; } return isMirror(root.left, root.right) }
# 动态规划
动态规划是算法设计中的一种思想,将一个问题分解为相互重叠的子问题,通过反复求解子问题来解决原来的问题
菲波那切数列
// 时间复杂度O(n) // 空间复杂度O(n) function fib(n) { let dp = [0, 1, 1]; for(let i = 3; i <= n; i++) { // 当前值等于前两个值之和 dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + dp[i - 2]; } return dp[n] }爬楼梯
// 正在爬楼梯, 需要n阶才能到达楼顶 // 每次只能爬 1 或者 2 个台阶, 有多少中不同的方法可以到达楼顶 // 时间复杂度 O(n) n是楼梯长度 // 空间复杂度 O(1) const climbStairs = n => { if(n < 2) return 1; let dp0 = 1; let dp1 = 1; for(let i = 2; i <= n; i++) { [dp0, dp1] = [dp1, dp1 + dp0] } return dp1; }
# 贪心算法
贪心算法是算法设计中的一种思想,期盼通过每个阶段的局部最优选择,从而达到全局最优,但是结果并不一定是最优
分发饼干
// 每个孩子都有一个胃口g. 每个孩子只能拥有一个饼干 // 输入: g = [1,2,3], s = [1,1] // 输出: 1 // 三个孩子胃口值分别是1,2,3 但是只有两个饼干,所以只能让胃口1的孩子满足 // 时间复杂度O(nlogn) // 空间复杂度O(1) const findContentChildren = function(g, s) { // 对饼干和孩子胃口进行排序 g.sort((a, b) => a - b); s.sort((a, b) => a - b); // 是第几个孩子 let i = 0; s.forEach(n => { // 如果饼干能满足第一个孩子 if(n >= g[i]) { i += 1; } }) return i; }买卖股票最佳时机Ⅱ
// 时间复杂度O(n) n为股票数量 // 空间复杂度O(1) const maxProfit = function(prices) { // 存放利润 const profit = 0; for(let i = 1; i < prices.length; i++) { // 不贪,如果有更高的利润直接卖出 if(prices[i] > prices[i - 1]) { profit += prices[i] - prices[i - 1]; } } return profit }优势洗牌
// 给定两个大小相等的数组 nums1 和 nums2,nums1 相对于 nums2 的优势可以用满足 nums1[i] > nums2[i] 的索引 i 的数目来描述。 // 返回 nums1 的任意排列,使其相对于 nums2 的优势最大化。 // 输入:nums1 = [2,7,11,15], nums2 = [1,10,4,11] // 输出:[2,11,7,15] const advantageCount = (nums1, nums2) => { let n = nums1.length; let idx1 = new Array(n).fill(0); let idx2 = new Array(n).fill(0); for(let i = 0; i < n; ++i) { idx1[i] = i; idx2[i] = i; } idx1.sort((i, j) => nums1[i] - nums1[j]); idx2.sort((i, j) => nums2[i] - nums2[j]); let ans = new Array(n).fill(0); let left = 0, right = n - 1; for(let i = 0; i < n; ++i) { if(nums1[idx1[i]] > nums2[idx2[left]]) { ans[idx2[left]] = nums1[idx1[i]]; ++left; } else { ans[idx2[right]] = nums1[idx1[i]]; --right; } } return ans; }
# 回溯算法
回溯算法是算法设计中的一种思想,一种渐进式寻找并构建问题解决方法的策略,会先从一个可能的动作开始解决问题,如不行,就回溯选择另外一个动画,直到找到一个解
全排列
// 输入 [1, 2, 3] // 输出 [[1, 2, 3], [1, 3, 2], [2, 1, 3], [2, 3, 1], [3, 1, 2], [3, 2, 1]] // 时间复杂度 O(n!) n! = 1 * 2 * 3 * ··· * (n-1) * n; // 空间复杂度 O(n) const permute = nums => { // 存放结果 const res = []; const backTrack = path => { // 递归结束条件 if(path.length === nums.length) { res.push(path); return; } // 遍历传入数组 nums.forEach(n => { //如果子数组中有这个元素就是思路,需要回溯回去走其他路 if(path.includes(n)) return; // 加入到子数组里 backTrack(path.concat(n)) }) } backTrack([]); return res; }子集
// 输入 [1,2,3] // 输出 [ [3], [1], [2], [1,2,3], [1,3], [2,3], [1,2], [] ] // 时间复杂度 O(2 ^ N) 每个元素都有两种可能 // 空间复杂度 O(N) const subsets = nums => { // 存放结果数组 const res = []; const backTrack = (path, l, start) => { if(path.length === l) { res.push(path); return; } for(let i = start; i < nums.length; i++) { backTrack(path.concat(nums[i], l, i+ 1); } } // 遍历输入数组长度 for(let i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) { backTrack([], i, 0) } return res; }
# 资料
← 二叉树相关概念 前端数据结构与算法入门 →