# 二叉树格式
var root = {
val:5,
left:{
val:4,
left:{
val: 3
},
right:{
val:2
}
},
right:{
val: 6,
left:{
val:7
},
right:{
val: 8
}
}
}
# 二叉树重建
前序遍历 preorder = [3,9,20,15,7]
中序遍历 inorder = [9,3,15,20,7]
var buildTree = function(preorder, inorder) {
if (preorder.length === 0) return null;
const cur = new TreeNode(preorder[0]);
const inndex = inorder.inndexOf(preorder[0]);
cur.left = buildTree(preorder.slice(1, index + 1), inorder.slice(0, index));
cur.right = buildTree(preorder.slice(index + 1), inorder.slide(index + 1));
}
# 二叉树的遍历
# 前序遍历
function rootTraverse(root) {
let res = [];
dfs(root, res);
return res;
}
function dfs(root, res){
if (root) { // 递归边界
res.push(root.val);
root.left && dfs(root.left, res);
root.right && dfs(root.right, res);
}
}
非递归
function rootRraverse(root) {
var result = [];
var strack = [root];
while(strack.length) {
let node = strack.pop();
result.push(node.val);
node.right && strack.push(node.right);
node.left && strack.push(node.left);
}
return result;
}
# 中序遍历
function rootTraverse(root) {
let res = [];
dfs(root, res);
return res;
}
function dfs(root, res){
if (root) {
root.left && dfs(root.left, res);
res.push(root.val);
root.right && dfs(root.right, res);
}
}
# 后序遍历
function rootTraverse(root) {
let res = [];
dfs(root, res);
return res;
}
function dfs(root, res){
if (root) {
root.left && dfs(root.left, res);
root.right && dfs(root.right, res);
res.push(root.val);
}
}
# 广度遍历
// count是一种形式,但是用shift() 也可以
function dfsRraverse(root) {
var res = [];
var strack = [root];
// var count = 0;
function dfs(root) {
// var node = strack[count];
var node = strack.shift();
if(node) {
res.push(node.val);
node.left && strack.push(node.left);
node.right && strack.push(node.right);
// count++
dfs();
}
}
dfs();
return res;
}
// [ 5, 4, 6, 3,2, 7, 8]
// 二
function levelOrder( root ) {
// write code here
let res = [];
function dfs(root, res, level) {
if (!root) return;
if (!res[level]) res[level] = [];
res[level].push(root.val);
root.left && dfs(root.left, res, level + 1)
root.right && dfs(root.right, res, level + 1)
}
dfs(root, res, 0);
return res;
}
console.log(levelOrder(root))
// while形式
function levelOrder(root) {
let res = [];
let stack = [root];
while(stack.length) {
let now = [];
let len = stack.length;
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
let node = stack.shift();
now.push(node.val);
node.left && stack.push(node.left)
node.right && stack.push(node.right)
}
res.push(now)
}
return res;
}
# 二叉树的锯齿形层序遍历
给你二叉树的根节点 root ,返回其节点值的 锯齿形层序遍历 。(即先从左往右,再从右往左进行下一层遍历,以此类推,层与层之间交替进行)。
var zigzagLevelOrder = function(root) {
if(!root) return [];
let flag = 1; // 控制当前层数是 顺序 还是 逆序 打印
let result = [], queue = [root];
while(queue.length) {
let len = queue.length; // 当前队列长度,即当前层数的结点个数
let now = [];
for(let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
let node = queue.shift();
// 我这里认定 flag === 1 时,是顺序打印,-1 是逆序
if(flag > 0) {
now.push(node.val); // 顺序是 push
} else {
now.unshift(node.val); // 逆序是 unshift
}
// 当前结点有左右子树,那就压入队列,等待下一层的 for 循环进行遍历
if(node.left) queue.push(node.left);
if(node.right) queue.push(node.right);
}
result.push(now);
flag = -flag;
}
return result;
};
# 二叉树最近的公共祖先
- 使用DFS的遍历思想进行遍历二叉树
- 如果为空节点或p节点或q节点,直接返回该节点
- 遍历的时候,看返回值,如果p和q都存在就返回当前的root节点,如果只有一个存在就反返回不为空的节点。
root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null, null,7,4];
p = 5, q = 1;
var lowestCommonAncestor = function(root, p, q) {
if(!root || root === p || root === q) return root;
let left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
let right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
if(!left) return right;
if(!right) return left;
return root
};
# 路径总和
给定一个二叉树和一个目标和,判断该树中是否存在根节点到叶子节点的路径,这条路径上所有的节点值等于目标和
var hasPathSum = function(root, sum) {
//如果不存在,表示不是叶子节点
if(!root) return false;
//如果是叶子节点,判断减去这个节点是否为o
if(!root.left && !root.right) return sum - root.val === 0;
//左右节点递归寻找一条存在的pathSum
return hasPathSum(root.left, sum-root.val) || hasPathSum(root.right, sum-root.val);
}
# 路径总和--二叉树中和为某一值的路径
/*
5
/ \
4 8
/ / \
11 13 4
/ \ / \
7 2 5 1
1. 标准的回溯法,每走一步(入path),expectedNum - root.val
2. 当前节点是叶子节点时,就判断值是不是能满足sum
3. 不等到节点都为空了
*/
function pathSum (root, sum) {
let res = [];
let path = [];
dfsHelper(root, path, sum, res);
return res;
}
function dfsHelper(root, path, expectedNum, res) {
//为空中止,判断叶子节点要比这提前
if (!root) {
return;
}
/*
如果是叶子节点,做判断
*/
if(!root.left && !root.right){
//此时还没入path
if(expectedNum === root.val){
res.push([...path,root.val]);
return
}
}
//当前节点入path
path.push(root.val);
//下一层需要的sum为 expectedNum - root.val,左右子***是一样的
dfsHelper(root.left, path, expectedNum - root.val, res);
dfsHelper(root.right, path, expectedNum - root.val, res);
path.pop(root.val);
}
# 路径总和--个数
给定一个二叉树的根节点root,和一个整数targetSum,求该二叉树里节点值的喝等于tagetSum的路径的数目。
路径不需要从根节点开始,也不需要在叶子节点结束,但是路径方向必须是向下的(只能从父节点到子节点)
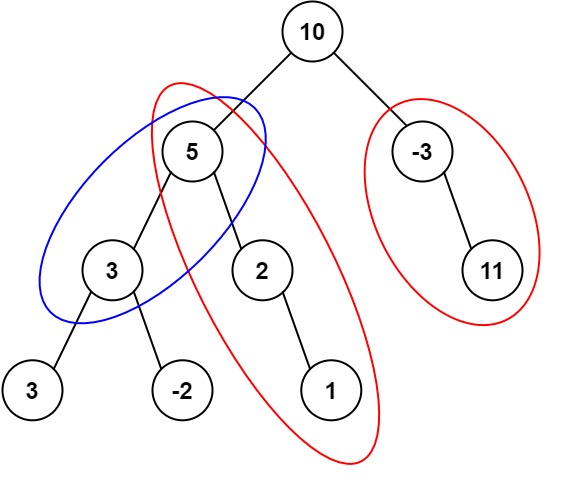
const pathSum = (root, targetSum) => {
if (!root) return 0;
let ret = rootSum(root, targetSum);
ret += pathSum(root.left, targetSum)
ret += pathSum(root.right, targetSum)
return ret;
}
const rootSum = (root, targetSum) => {
if (!root) return 0;
let ret = 0;
if (targetSum - root.val == 0) {
ret++;
}
ret += rootSum(root.left, targetSum - root.val);
ret += rootSum(root.right, targetSum - root.val);
return ret;
}
# 二叉树中最大路径和
路径 被定义为一条从树中任意节点出发,沿父节点-子节点连接,达到任意节点的序列。同一个节点在一条路径序列中 至多出现一次 。该路径 至少包含一个 节点,且不一定经过根节点。
路径和 是路径中各节点值的总和。
给你一个二叉树的根节点 root ,返回其 最大路径和 。
输入:root = [1,2,3]
输出:6
解释:最优路径是 2 -> 1 -> 3 ,路径和为 2 + 1 + 3 = 6
解答
const maxPathSum = (root) => {
let maxSum = Number.MIN_SAFE_INTEGER;//初始化最大路径和
const dfs = (root) => {
if (root == null) {//遍历节点是null 返回0
return 0;
}
const left = dfs(root.left); //递归左子树最大路径和
const right = dfs(root.right); //递归右子树最大路径和
maxSum = Math.max(maxSum, left + root.val + right); //更新最大值
//返回当前子树的路径和 分为走左边、右边、不动 3种情况
const pathSum = root.val + Math.max(0, left, right);
return pathSum < 0 ? 0 : pathSum;
};
dfs(root);
return maxSum;
};
# 树的子结构
输入两个二叉树A和B,判断B是不是A的子结构 力扣 (opens new window)
// 是否是相同的树
var isSameTree = function(p, q) {
if(p == null && q == null)
return true;
if(p == null || q == null)
return false;
if(p.val != q.val)
return false;
return isSameTree(p.left, q.left) && isSameTree(p.right, q.right);
};
//判断B是否是A的子结构
const isSubStructure = (A, B) => {
if(!A || !B) {
return false;
}
return isSameTree(A, B) || isSubStructure(A.left, B) || isSubStructure(A.right, B)
}
const isSameTree = (A,B) => {
if(!B) return true;
if (!A) return false;
if (A.val !== B.val) return false;
return isSameTree(A.left, B.left) && isSameTree(A.right, B.right)
}
# 将有序数组转换
将一个按照升序排列的有序数组,转换成一颗高度平衡的二叉树。
给定有序数组:[-10,-3,0,5,9]
0
/ <br/>
-3 9
/ <br/>
-10 5
var soortedArrayToBST = function(nums) {
if (nums.length) return null;
let creatTree = (left, right) => {
if(left > right) return null;
let mid = Math.floor((left + right) / 2);
let root = new TreeNode(nums[mid]);
root.left = createTree(left, mid -1);
root.right = createTree(mid + 1, right);
return root;
}
return creatTree(0, nums.length - 1);
}
# 不同的二叉搜索树
给定一个整数n,求以1...n为节点组成的二叉搜索树有多少种
** 示例 **
输入:3
输出:5
解释:
给定n = 3,一共有五种不同的结构的二叉搜索树
1 3 3 2 1
\ / / / \ \
3 2 1 1 3 2
/ / \ \
2 1 2 3
** 代码 **
//动态规划
var numTrees = function(n) {
const dp = new Array(n + 1).fill(0);
dp[0] = 1;
dp[1] = 1;
for(let i = 2; i <= n; ++i) {
for (j = 1; j <= i; ++i) {
dp[i] += dp[j - 1] * dp[i -j];
}
}
return dp[n];
}
# 右明树
- DFS
var rightSideView = function(root) {
if (!root) return [];
let arr = [];
dfs(root, 0, arr);
return arr;
}
function dfs(root, step, res) {
if (root) {
if (res.length === step) {
res.push(root.val);
}
dfs(root.right, step + 1, res);
dfs(root.left, step + 1, res);
}
}
- BFS
var rightSideView = function(root) {
if (!root) return [];
let queue = [root];
let arr = [];
while(queue.length > 0) {
let len = queue.length;
while (len) {
let node = queue.shift();
if (len === 1) arr.push(node.val);
if (node.left) queue.push(node.left);
if (node.right) queue.push(node.right);
len--;
}
}
return arr;
}
# 二叉树的最大深度
给定一个二叉树,找出其最大深度。
二叉树的深度为根节点到最远子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
说明:叶子节点是指没有节点的节点
实例:给定二叉树[3,9,20,null, null, 15,7]
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
题解
// 1.递归
// 树的深度和它的左右子树的深度有关
// 一个树的最大深度=根节点的高度+左右子树的最大深度中较大的那个
const maxDepth = (root) => {
if(root === null) return 0;
const leftMaxDepth = maxDepth(root.left);
const rightMaxDepth = maxDepth(root.right);
return 1 + Math.max(leftMaxDepth, rightMaxDepth);
}
// 2.BFS
const maxDepth = (root) => {
if(!root) return 0;
let stack = [root];
let count = 1;
while(stack.length) {
const levelNum = stack.length;
for (let i = 0; i < levelNum; i++) {
const node = stack.shift();
node.left && stack.push(node.left);
node.right && stack.push(node.right);
}
if (stack.length) count++;
}
return count;
}
# 二叉树的最小深度
输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
输出:2
示例 2:
输入:root = [2,null,3,null,4,null,5,null,6]
输出:5
var minDepth = function(root) {
if (!root) return 0; // 把根节点传进去
const q = [[root, 1]]; // 队列
while(q.length) {
const [n, l] = q.shift();
if (!n.left && !n.right) return l;
if (n.left) q.push([n.left, l + 1]);
if (n.right) q.push([n.right, l + 1]);
}
}
# 对称二叉树
1
/ \
2 2
/ \ / \
3 4 4 3
观察上面的对称二叉树,判断二叉树是否是镜像的,我们需要比较子树的对称位置是否相同。
即左子树的左侧与右子树右侧,左子树右侧与右子树左侧。
迭代法
function isSymmetric(root) {
if (!root) return true;
const isMirror = (l, r) => {
const queue = [l, r];
while (queue.length) {
const u = queue.shift();
const v = queue.shift();
if (u == null && v == null) continue;
if (u == null || v == null) {
return false;
}
if (u.val !== v.val) {
return false;
}
queue.push(u.left, v.right);
queue.push(u.right, v.left);
}
return true;
}
return isMirror(root.left, root.right)
};
# 翻转二叉树
翻转一棵二叉树。
示例:
输入:
4
/ \
2 7
/ \ / \
1 3 6 9
输出:
4
/ \
7 2
/ \ / \
9 6 3 1
// 编码
const invertTree = function(root) {
if (root === null) return null;
const left = invertTree(root.left);
const right = invertTree(root.right);
root.left = right;
root.right = left;
return root;
}