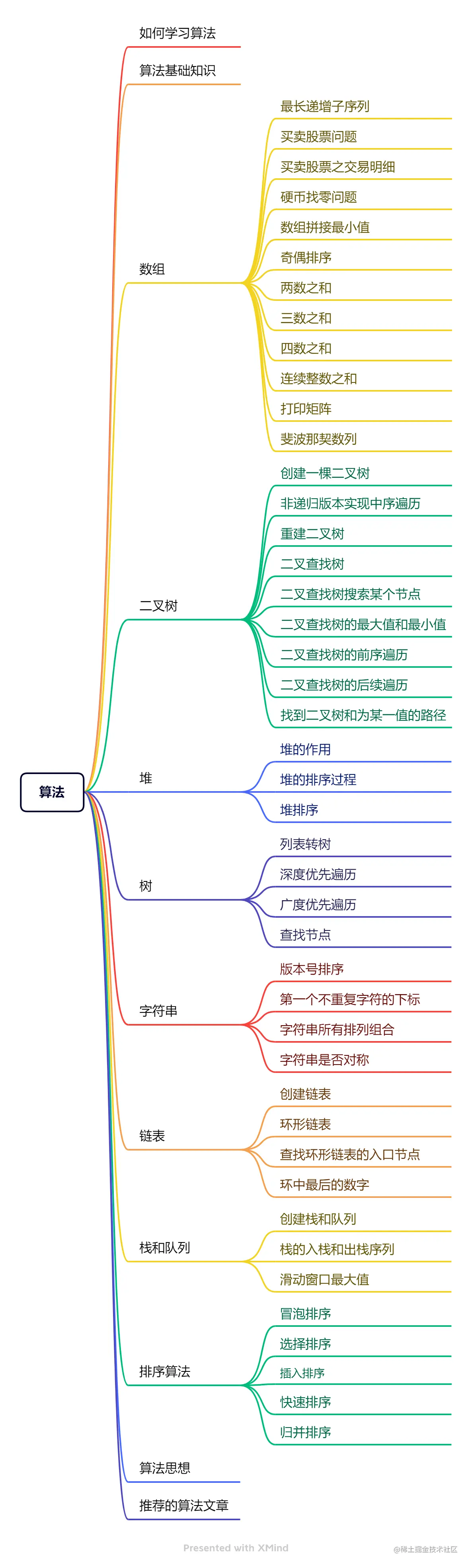
# 算法
# 如何学习算法
先掌握对应的数据结构
以面试中最常见的二叉树为例
先了解如何创建一个二叉树,通过创建的过程,加深对该数据机构的理解
分类练习
分类练习,即按照每种数据结构进行统一练习
例如:这段时间只练习二叉树的题目,通过集中的训练,对二叉树有整体的认知。了解前、中、后序遍历的特点,了解二叉搜索树,了解各种题型等体系知识
# 算法基础知识
时间复杂度
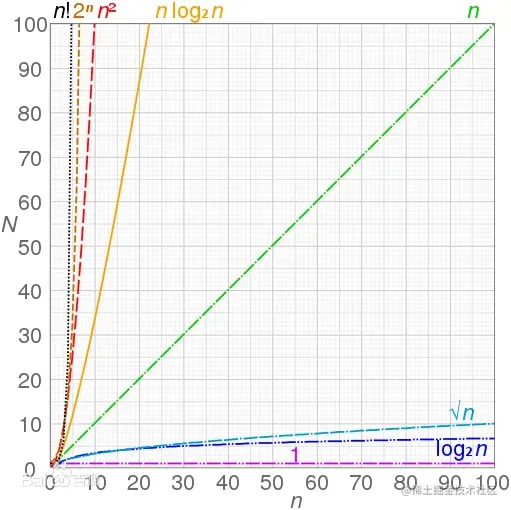
表示代码执行的次数,时间与算法中语句执行次数成正比例,哪个算法中执行语句次数多,它花费的时间就越长,时间复杂度是取代码中最复杂的代码来计算的
时间复杂度按时间的大小,从小到大排序依次是:O(1) < O(logn) < O(n) < O(nlogn) < O(n2) < O(n3) < O(2n) < O(!n)
空间复杂度
在算法运算过程中用到的额外的存储空间(不包含原始值的内存大小),反映的内存占用的趋势,而不是具体内存
最经典的场景:就是利用空间去换时间,降低时间复杂度,减少计算时间
# 前端 数据结构
数组、栈、队列、树、堆、链表、哈希表、图
# 数组
数组是最简单的、也是最常用的数据结构
数组是可以在内种连续存储多个元素的机构,在内存中分配也是连续的
特点:查询快,增删慢
- 查询快:数组的地址是连续的,我们通过数组的首地址可以找到数组,通过数组的索引可以快速查找某个元素
- 增删慢:数组的长度是固定的,我们要增加/删除元素,必须创建一个新的数组,把原来的数据复制过来???
# 最长递增子序列
该算法在vue3 diff算法中有用到,作用是找到最长递归子序列后,可以减少子元素的移动次数
一个整数数组nums,找出其中一组最长递增子序列的值
最长递增自学列是指:子序列中的所有元素单调自增.例如[3,5,7,1,2,8]的LIS是[3,5,7,8]
// 该算法用的是动态规划的思想,时间复杂度N<sup>2</sup>,并不是最优算法,最优算法应该是二分查找,最优时间复杂度为nlongn
function lengthOfLIS(nums) {
if(!nums.length) return 0;
// 创建一个和原数组登场的数组dp,用来存储每一项的最长递增序列,比如[1,2,2]表示第二项和第三项的最长递增序列都为2
// 该数组每一项初始值都为1,记录当前项的最长递增序列,后面的项会在当前项的最长递增序列个数进行累加
const dp = new Array(nums.length).fill(1);
// 双层for循环,每一项都和之前的所有项一一进行比较,计算出该项的最长递增子序列个数,存储到dp
for(let i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
// 当前项依次和之前的每一项进行比较,累加处当前项的最长递增子序列
for(let j = 0; j < i; j++) {
if(nums[i] > nums[j]) {
// 比较当前项已有的最大值和之前项最大值,比如当比较到第三项[1,2,2]时,如第三项比第二项大,所以第三项的计算结果为[1,2,3]
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i], dp[j] + 1);
}
}
}
// 取出一组最长递增子序列的具体值(注意:最长递增子序列有可能有多组值,这里是只取出其中一组值)
// 找到dp中的最大值,该值就是nums的最长递增子序列的个数
let max = Math.max(...dp);
let result = [];
for(let i = max; i >= 1; i--) {
// 倒序遍历,根据长度获取对应的值
findArrNode(dp, i, result, nums);
}
return result;
}
function findArrNode(dp, value, result, arr) {
// 找到符合条件最后一项的下标,这样才能保证数组的顺序是正确的
let index = dp.lastIndexOf(value);
// 存储对应的值
result.unshift(arr[index]);
// 对dp进行截取,保证只取最大项之前的数据
dp.length = index + 1;
}
// 测试
console.log(lengthOfLIS([9, 1, 7, 10, 4, 8, 5, 2])); // [1, 4, 5]
console.log(lengthOfLIS([1, 4, 3, 5, 2, 6, 0])); // [1, 3, 5, 6]
# 买卖股票问题
给定一个整数数组,其中第i个元素代表了第i天的股票价格;
非负整数fee代表了交易股票的手续费用,求返回获得利润的最大值
例如数组为:[1,12,13,9,15,8,6,16], fee为2,求获得利润的最大值
注:每笔买卖都需要支付一次手续费
/**
* 贪心算法求解
* @param {array} list --股票每天价格列表
* @param {number} fee -- 手续费
*/
function buyStock(list, fee) {
// min为当前的最小值,即买入值
let min = list[0], sum = 0;
for(let i = 1; i < list.length; i++) {
if(list[i] < min) {
// 寻找数组最小值
min = list[i];
} else {
// 计算如果当天卖出是否赚钱
let temp = list[i] - min - fee;
if(temp > 0) {
// 赚钱 存数据
sum += temp;
// 关键代码:重新计算min,分两种情况,如果后续继续涨,则默认继续持有,若后面跌,则以后面的价格重新买入
min = list[i] - fee;
}
}
}
return sum; // 12-(12-2) -2 == 12-12+2-2
}
console.log(buyStock([1, 12, 13, 9, 15, 8, 6, 16], 2)); // 22
# 买卖股票之交易明细
继续研究买卖股票问题
通过上题,我们知道[1, 12, 13, 9, 15, 8, 6, 16]最终的结果为22
但具体的交易明细是什么,哪几天发生了交易,怎么验证22的结果是否正确呢?
思路
- 增加result对象,把每笔赚钱的交易都记录下来
- 新增minIndex属性,用来记录每次买入值(最小值)的变化
- 当minIndex不变时,用新的记录替换掉老的记录
- 遍历result对象,取出所存储的交易明细
/**
* 贪心算法求解交易明细
* @param {array} list- 股票每天价格列表
* @param {number} fee - 手续费
*/
function buyStock(list, fee) {
// 增加result对象,把眉笔交易的记录都记录下来
let result = {};
let min = list[0];
// 增加minIndex 用来记录每次买入值(最小值)的变化
let minIndex = 0;
let sum = 0;
for(let i = 1; i < list.length; i++) {
if(list[i] < min) {
minIndex = i;
min = list[i];
} else {
let temp = list[i] - min - fee;
if(temp > 0) {
sum += temp;
min = list[i] - fee;
// 赚钱存数据
// 当minIndex不变时,用新的记录替换老的记录
result[minIndex] = [list[minIndex], list[i]];
}
}
}
let arr = [];
Object.keys(result).forEach(key => {
arr.push(result[key]);
})
return {
sum, arr
}
}
console.log(buyStock([1, 12, 13, 9, 15, 8, 6, 16], 2));
// 打印结果: {sum: 22, arr: [[1, 13], [9, 15], [6, 16]]}
3次交易明细
1买入,13卖出;
9买入,15卖出;
6买入,16卖出
22 = (13 - 1 - 2) + (15 - 9 -2) + (16 - 6 - 2)
# 硬币找零问题
给定不同面额的硬币,coins和一个总金额amount
编写一个函数来计算可以凑成总金额所需的最少硬币个数,如果没有任何一种硬币总和能组成总金额,返回-1
示例:输入coins= [1,2,5],amount = 11 输出3
function findCoins(coins, amount) {
if(coins.length === 0) return -1;
// 用于保存每个目标总额对应的最小硬币个数
const f = [];
f[0] = 0;
// 遍历[1, amount]这个区间的硬币总数
for(let i = 1; i <= amount; i++) {
// 求的是最小值,因此我们预设为无穷大,确保它一定会被最小的数更新
f[i] = Infinity;
// 循环遍历每个可用硬币的面额
for(let j = 0; j < coins.length; j++) {
if(i - coins[j] >= 0) {
f[i] = Math.min(f[i], f[i - coins[j]] + 1);
}
}
}
if(f[amount] === Infinity) {
return -1;
}
return f[amount]
}
console.log(findCoins[1,2,5], 11); // 3
// 递归
function findCoins(coins, amount) {
const dfs = (n) => {
if(n === 0) return 0;
if(n < 0) return 0
let res = Infinity
for(let coin of coins) {
let ressum = dfs(n - coin)
if(res < 0) continue;
res = Math.min(res, 1 + ressum)
}
return res === Infinity ? -1 : res;
}
return dfs(amount)
}
console.log(findCoins([1, 2, 5], 11)); // 3
// 测试-组合
function findCoins(coins, amount) {
let could = [];
let res = [];
const dfs = (n, could, res) => {
if(n <= 0) {
res.push(could.slice(0))
return;
}
for(let coin of coins) {
could.push(coin);
dfs(n - coin, could, res)
could.pop();
}
}
dfs(amount, could, res)
return res;
}
console.log(findCoins([1, 2, 5], 11)); // 3
LeetCode 19.凑零钱问题 动态规划 (opens new window)
# 数组拼接最小值
一个正整数数组,把数组里所有数字拼接起来排成一个数,打印能拼接处的所有数字中最小的一个
如[3,45,12] 拼接的最小值为12345
- 思路:利用sort排序:a和b两个数字可以有两种组合:ab和ba,例如ab < ba则ab排在ba前面
function printMinNumber(arr) {
if(!arr || arr.length === 0) return null;
// sort底层是快排
return arr.sort(compare).join('')
}
// 找到ab和ba这两种组合的最小值
function compare(a, b) {
let front = `${a}${b}`;
let after = `${b}${a}`;
return front - after;
}
let arr = [3, 45,12];
console.log(printMinNumber(arr)); // 123456
# 奇偶排序
一个整数数组,实现一个函数来调整该数组中数字的顺序,使得所有的奇数位于数组的前半部分,所有的偶数位于数组的后半部分
- 思路:设定两个指针
- 第一个指针start,从数组第一个元素触发,向尾部前进
- 第二个指针end,从数组的最后一个元素触发,向头部前进
- start遍历到偶数,end遍历到奇数,交换两个数的位置
- 当start > end时完成交换
function exchangeOddEven(arr) {
let start = 0;
let end = arr.length - 1;
// 当start > end时完成交换
while(start < end) {
// 找到第一个奇数
while(arr[start] % 2 === 1) {
start++
}
while(arr[end] % 2 === 0) {
end--;
}
if(start < end) {
[arr[start], arr[end]] = [arr[end], arr[start]]
}
}
return arr;
}
let test = [2, 4, 5, 3, 1];
console.log(exchangeOddEven(test)); // [1, 3, 5, 4, 2]
# 两数之和
// 时间复杂度O(n),空间复杂度O(n);
function twoSum(arr, target) {
if(Array.isArray(arr)) {
let map = {};
for(let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if(map[target - arr[i]] !== undefined) {
return [target - arr[i], arr[i]]
} else {
map[arr[i]] = i;
}
}
} else {
return [];
}
}
# 三数之和
function findThree(arr, target) {
arr.sort();
let result = [];
for(let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if(i && arr[i] === a[i - 1]) continue;
let left = i + 1;
let right = arr.length - 1;
while(left < right) {
let sum = arr[i] + arr[left] + arr[right];
if(sum > target) {
right--;
} else if(sum < target) {
left++;
} else {
result.push([arr[i], arr[left++], arr[right--]]);
while(arr[left] === arr[left - 1]) {
left+=;
}
while(arr[right] === arr[right + 1]) {
right--;
}
}
}
}
return result;
}
# 四数之和
给定一个整数数组nums,判断 nums 中是否存在四个元素a,b,c,d ,使得 a + b + c + d = target,找出所有满足条件且不重复的四元组合
思路
到这里其实我们就能发现一些规律,可以像三数之和那样,通过大小指针来逼近结果,从而达到降低一层时间复杂度的效果(重点:将4个数相加,转化为三个数,降低层级)
不管是几数之和,都可以用这种方法来进行降级优化
function findFour(arr, target) {
if(arr.length < 4) return [];
let result = [];
arr.sort();
// 最外层控制循环次数,循环次数为arr.length - 3;
for(let i = 0; i < arr.length - 3; i++) {
// 跳过数组中,重复的起始值
if(i && arr[i] === arr[i - 1]) continue;
// 因为数组已进行排序,所以一但超过目标值,那么以后的值也都比目标值大,所以可以直接结束这一轮循环
if(arr[i] + arr[i + 1] + arr[i + 2] + arr[i + 3] > target) break;
for(let j = i + 1; j < arr.length - 2; j++) {
// 注意范围,第二个值的最小值是倒数第三位(以下代码和三个数求和逻辑一直)
// 跳过数组中,第二个重复的
if(j > i + 1 && arr[j] === arr[j - 1]) continue;
// 第三个数的下标
let left = j + 1;
let right = arr.length - 1;
while(left < right) {
let sum = arr[i] + arr[j] + arr[left] + arr[right];
if(sum > target) {
right--;
} else if(sum < target) {
left++;
}else {
// 坑点,注意添加后,left++, right--, 确保循环继续执行
result.push([arr[i], arr[j], arr[left++], arr[right--]]);
while (arr[left] === arr[left - 1]) {
// 跳过重复的值
left++;
}
while (arr[right] === arr[right + 1]) {
// 跳过重复的值
right--;
}
}
}
}
}
return result;
}
console.log(findFour([2, 1, 5, 4, 3, 6, 0, 7], 10)); // [0, 1, 2, 7] [0, 1, 3, 6] [0, 1, 4, 5] [0, 2, 3, 5] [1, 2, 3, 4]
# 连续整数之和
输入一个正整数S,打印出所有和为S的连续整数序列
例如:输入15,连续整数序列有:1+2+3+4+5 = 4 + 5 + 5 = 7 + 8 = 15.所以打印出3个连续序列1-5,,5-6和7-8
- 思路
- 创建一个容器child,用于表示当前的子序列,初始元素为1,2
- 记录子序列的开头元素small和末尾元素big
- big向右移动子序列末尾增加一个数;smal向右移动子序列开头减少一个数
- 当子序列的和大于目标值,small向右移动,子序列和小于目标值,big向右移动
function FindContinuousSequence(sum) {
let result = []
// 记录当前的结果
let child = [1,2];
let small = 1; // 初始值1
let big = 2;
let currentSum = 3; // 当前数字之和
while(big < sum) {
// big等于sum时,child中只剩一个数,不满足连续整数序列的要求,结束循环
while(currentSum < sum && big < sum) {
child.push(++big);
// currentSum为当前child的和
currentSum += big;
}
console.log(child)
while(currentSum > sum && small < big) {
child.shift();
// 因为删除了最小值,所以small也要响应变化,增加1
currentSum -= small++;
}
if(currentSum === sum && child.length > 1) {
// child.length 大于1,剔除一个数等于sum的情况
// child.slice返回一个新数组
result.push(child.slice());
child.push(++big);
currentSum += big;
}
}
return result;
}
console.log(FindContinuousSequence(15)); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] [4, 5, 6] [7, 8]
# 打印矩阵
输入:
[
[1,2,3],
[4,5,6],
[7, 8,9]
]
输出: [1,2,3,6,9,8,7, 4,5]
题目要求是按照顺时针的顺序,从外向内遍历每一个元素,并将他们俺顺序返回出来
function printMatrix(arr) {
// map函数用来完成当前矩阵最外一圈的遍历
// @param1 {Array} 二维数组 arr表示当前矩阵
// @param2 {Array} 一维数组 result用来存储遍历结果
let map = (arr, result) => {
// 矩阵的高度即行数
let n = arr.length;
// 遍历矩阵的每一行
for(let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// 若第一行,按顺序插入
if(i === 0) {
result = result.concat(arr[i]);
} else if(i === n - 1) {
// 若最后一行,倒序插入
result = result.concat(arr[i].reverse())
} else {
// 若中间行 插入改行最后一个元素,并将该元素从矩阵中删除
result.push(arr[i].pop());
}
}
// 将已经遍历的第一行和最后一行从矩阵中删除
arr.pop();
arr.shift();
// 遍历插入最左侧一列 此时删除首位两行后矩阵高度已变为n- 2;
for(let j = n - 3; j >= 0; j--) {
// 避免arr[j]长度为空时插入undefined
if(arr[j].length) {
result.push(arr[j].shift())
}
}
// 截止条件 矩阵有元素就继续递归
if(arr.length) {
// 把已有遍历元素删除的矩形进行递归
return map(arr, result);
} else {
return result;
}
}
return map(arr, [])
}
let matrix = [
[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6],
[7, 8, 9]
];
console.log(printMatrix(matrix)); // [1, 2, 3, 6, 9, 8, 7, 4, 5]
# 菲波那切数列
从第3项开始,当前项等于前两项之和:1 1 2 3 5 8 13 21……
使用动态规划,将复杂的问题拆分,也就是:F(N) = F(N - 1) + F(N - 2),然后用数组将已经计算过的值存起来
function fib(n) {
// 使用dp数组,将之前计算的结果存起来,防止栈溢出
let dp = [];
dp[0] = 1n; // bigint 用来表示超过2^53 -1的大整数
dp[1] = 1n;
for(let i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + dp[i - 2]
}
return dp[n]
}
console.log(fib(1000))
# 二叉树
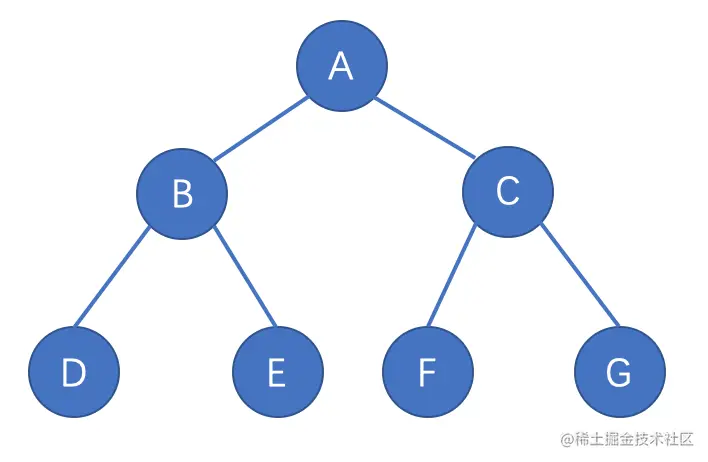
二叉树是树结构中一种典型的结构,每个节点最多只能有两个子节点,一个是左侧子节点,一个是右侧子节点
# 二叉树遍历的规律
- 前序遍历:根节点 + 左子树前序遍历 + 右子树前序遍历
- 中序遍历: 左子树中序遍历 + 根节点 + 右子树中序遍历
- 后序遍历: 左子树后续遍历 + 右子树后续遍历 + 根节点
# 创建一颗二叉树
要求:若新节点的值比父节点小,则放到父节点的左子树上;反之放到右子树上
class Node {
constructor(data, left = null, right = null) {
this.data = data;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
// 构建二叉树
class Tree {
constructor() {
this.root = null;
}
insert(data) {
var node = new Node(data, null, null);
// 创建根节点
if(!this.root) {
this.root = node;
return;
}
var current = this.root;
var parent = null;
while(current) {
parent = current;
// 值比父节点小,放到父节点左子树上
if(data < current.data) {
current = current.left;
// 找到最左侧的节点,将新的节点设置为该节点的左子树节点
if(!current) {
parent.left = node;
return;
}
} else {
// 值比父节点大,放到父节点的有字数上
current = current.right;
if(!current) {
parent.right = node;
return;
}
}
}
}
// 定义前序遍历的方法
static preOrder(node, arr = []) {
if(node) {
arr.push(node.data);
this.preOrder(node.left, arr);
this.preOrder(node.right, arr);
}
return arr;
}
// 定义中序遍历的方法
static middleOrder(node, arr = []) {
if (node) {
this.middleOrder(node.left, arr);
arr.push(node.data);
this.middleOrder(node.right, arr);
}
return arr;
}
// 定义后序遍历的方法
static laterOrder(node, arr = []) {
if (node) {
this.laterOrder(node.left, arr);
this.laterOrder(node.right, arr);
arr.push(node.data);
}
return arr;
}
// 获取二叉树的最大层级
static getDeep(node, deep = 0) {
if(!node) return deep;
deep++;
// 获取左子树的层级
let left = this.getDeep(node.left, deep);
// 获取右子树的层级
let right = this.getDeep(node.right, deep);
// 去层级最大值
return Math.max(left, right)
}
}
// 创建二叉树,依次插入新节点
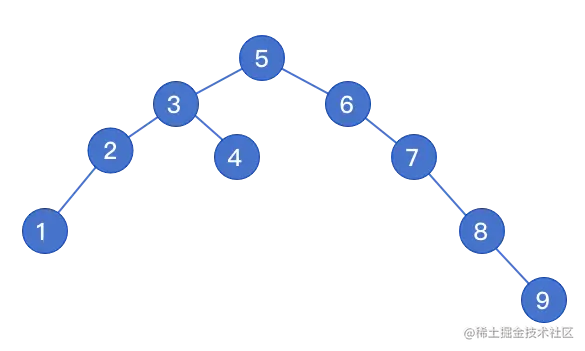
var t = new Tree();
t.insert(5);
t.insert(3);
t.insert(6);
t.insert(2);
t.insert(4);
t.insert(7);
t.insert(8);
t.insert(1);
t.insert(9);
// 打印二叉树
console.log(t);
// 前序遍历 [5, 3, 2, 1, 4, 6, 7, 8, 9]
console.log(Tree.preOrder(t.root));
// 中序遍历 [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
console.log(Tree.middleOrder(t.root));
// 后序遍历 [1, 2, 4, 3, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5]
console.log(Tree.laterOrder(t.root));
// 获取二叉树的最大层级: 5
console.log(Tree.getDeep(t.root));
# 中序遍历的两种方式
- 方式一:递归版本,如上文的middleOrder方法
- 方式二:非递归版本(回溯算法)实现中序遍历
非递归版本的好处:避免循环递归栈溢出的情况,效率更高
function middleTraverse(root) {
let result = [];
const stack = [];
let current = root;
while(current || stack.length > 0) {
// 找到左侧节点存到栈中
while(current) {
stack.push(current);
current = current.left;
}
// 节点出栈
current = stack.pop();
// 存储该节点的值
result.push(current.data);
// 获取该节点右子树节点
current = current.right;
}
return result;
}
// t 为上文创建的二叉树
console.log(middleTraverse(t.root));
// 打印结果: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
# 重建二叉树
输入某二叉树的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果,重建出该二叉树
// 重建二叉树
function reConstruction (pre, mid) {
if(pre.length === 0) return null;
// 前序遍历长度为1时,该节点为叶子节点
if(pre.length === 1) return new Node(pre[0]);
// 前序遍历的第一个值为根节点
const value = pre[0];
// 找到根节点在中序遍历的位置
const index = mid.indexOf(value);
// 将中序遍历 分为左子树中序遍历 和右子树中序遍历
const midLeft = mid.slice(0, index);
const midRight = mid.slice(index + 1);
// 左子树前序遍历的长度为index
// 将前序遍历 分为左子树前序遍历 和 右子树前序遍历
const preLeft = pre.slice(1, index + 1);
const preRight = pre.slice(index + 1);
// 创建根节点
const node = new Node(value);
// 利用左子树中序遍历 + 左子树前序遍历,递归创建左子树节点
node.left = reConstruction(preLeft, midLeft);
// 递归创建右子树节点
node.right = reConstruction(preRight, midRight);
return node;
}
class Node {
constructor(data, left = null, right = null) {
this.data = data;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
reConstruction([1, 2, 4, 7, 3, 5, 6, 8], [4, 7, 2, 1, 5, 3, 8, 6]);
# 二叉查找树
二叉查找树(BST)是二叉树的一种,特点是所有的左节点比父节点的值小,所有的右节点比父节点的值大,并且任意左、右子树也分别是二叉查找树
主要作用是搜索和动态排序
二叉查找树搜索某个节点
// 查找一个节点 function findNode(data, node) { if(node) { if(data === node.data) { return node; } else if(data < node.data) { return this.findNode(data, node.left) } else { return this.findNode(data, node.right); } } else { return null; } } // 查找值为6的节点 // t 为上文创建的二叉树 console.log(findNode(6, t.root))二叉查找树的最大值和最小值
// 最右侧的节点为二叉查找树的最大值 // 最左侧的节点为二叉查找树的最小值 // 最大值:最右侧的节点 function getMax(root) { let max = null; let current = root; while(current) { max = current.data; current = current.right; } return max; } // 最小值:最左侧的节点 function getMix(root) { let mix = null; let current = root; while(current) { mix = current.data; current = current.left; } return mix; } console.log(getMax(t.root), 'max'); // 9 console.log(getMix(t.root), 'min'); // 9判断数组是否为二叉查找树的前序遍历结果
给你一个整数数组,判断改数组是不是某二叉查找树的前序遍历结果,如果是输出true,否则输出false
// 判断一个整数数组,是否为某二叉查找树的前序遍历的结果 function preOrderOfBST(list) { if(list && list.length > 0) { // 前序遍历,第一个值为根节点 var root = list[0]; // 找到数组中,第一个比根节点大的节点,即为右子树的节点 for(var i = 0; i < list.length; i++) { if(list[i] > root) { break; } } // 遍历右子树的节点,要求所有右子树的节点都比根节点大 for(let j = i; j < list.length; j++) { if(list[j] < root) { return false; } } var left = true; // 同理,递归判断左子树是否符合二叉搜索树的规则 if (i > 1) { left = preOrderOfBST(list.slice(1, i + 1)); } var right = true; // 递归判断右子树是否符合二叉搜索树的规则 if (i < list.length) { right = preOrderOfBST(list.slice(i, list.length)); } // 左、右子树 都符合要求,则是一个二叉搜索树 return left && right; } } console.log(preOrderOfBST([5, 3, 2, 1, 4, 6, 7, 8, 9])); // true判断数组是否为二叉搜索树的后续遍历结果
给一个整数数组,判断该数组是不是某二叉搜索树的后续遍历的结果如果是则输出true,否则输出false
// 判断一个整数数组,是否为某二叉搜索树的后序遍历的结果 function laterOrderOfBST(list) { if (list && list.length > 0) { // 后续遍历,最后一个节点为根节点 var root = list[list.length - 1]; for (var i = 0; i < list.length - 1; i++) { if (list[i] > root) { break; } } for (let j = i; j < list.length - 1; j++) { if (list[j] < root) { return false; } } var left = true; // 判断左子树 if (i > 0) { left = laterOrderOfBST(list.slice(0, i)); } var right = true; // 判断右子树 if (i < list.length - 1) { right = laterOrderOfBST(list.slice(i, list.length - 1)); } return left && right; } } console.log(laterOrderOfBST([1, 2, 4, 3, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5])); // true
# 找到二叉树和为某一值的路径
利用回溯算法:如果不符合要求,退回来,换一条路再试
找到和为11的所有路径:结果为[5, 3, 2, 1], [5, 6]

function findPath(node, num, stack = [], sum = 0, result = []) {
stack.push(node.data);
sum += node.data;
if(sum === num) {
result.push(stack.slice())
}
if(node.left) {
findPath(node.left, num, stack, sum, result);
}
if(node.right) {
findPath(node.right, num, stack, sum, reuslt);
}
// 回溯算法:不符合要求,退回来,换一条路再试
// 叶子节点直接pop;子节点中的所有节点递归完成后在pop
stack.pop();
return result;
}
console.log(findPath(t.root, 11)) // [5, 3, 2, 1], [5, 6]
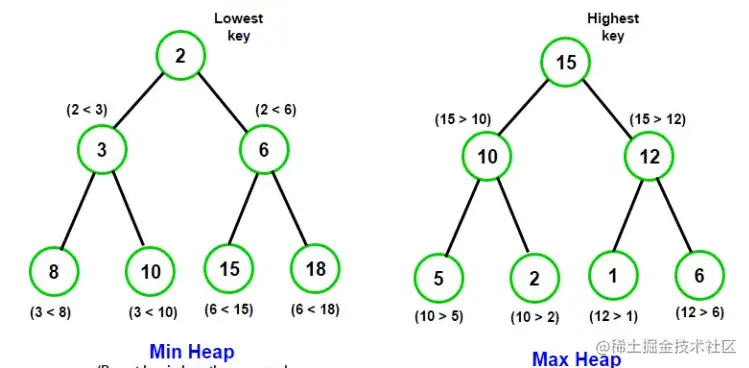
# 堆
堆实际上是一颗完全二叉树
- 大顶堆: 每个节点元素值不小于其子节点
- 小顶堆:每个节点元素值不大于其子节点
# 堆的作用
在庞大的数据中,找到最大的m个数或者最小的m个数,可以借助堆来完成这个过程,时间复杂度为nlongm
如果先排序,在取前m个数,最小时间复杂度nlongn
nlongm < nlongn,堆排序时间复杂度更优
# 堆节点与其叶子节点的规律
- 堆中父节点为k,它的左叶子结点下标为2k + 1, 右子节点是2k + 2;
- 所有序号大于length / 2 的节点都是叶子节点, 0 到length / 2 - 1为父节点
# 堆的排序过程

# 堆排序
从一堆数中,找到前m个最小值
如图,从下面的大顶堆中,找到前4个最小值,结果为[6,5,2,1]
function heapSort(list, m) {
if(m > list.length) {
return [];
}
createHeap(list, m);
for(let i = m; i < list.length; i++) {
if(list[i] < list[0]) {
// 找到前m个数的最小值,依次将最小值放到最前面
[list[i], list[0]] = [list[0], list[i]];
ajustHeap(list, 0, m);
}
}
// 取出前m个数
return list.splice(0, m)
}
// 构建大顶堆(构建的顺序是从下往上,先找到最后一个父节点,然后从最后一个父节点开始构建,然后依次往上构建,将最大值逐步替换成根节点)
function createHeap(arr, length) {
// 找到堆中所有的非叶子节点(找到最后一个叶子节点,该节点之前都是非叶子节点)
for(let i = Math.floor(length / 2) - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
// 堆中,父节点为i,则子节点为2 * i+ 1 、2 * i+ 2;反过来,知道了子节点为length,则最后一个子节点为Math.floor(length / 2) - 1;
ajustHeap(arr, i, length);
}
}
// 调整大顶堆
function ajustHeap(arr, index, length) {
for(let i = 2 * index + 1; i < length; i = 2 * i + 1) {
// 父节点为i, 则子节点为2 * i+ 1;
if(i + 1 < length && arr[i + 1] > arr[i]) {
// 找到arr[i + 1] 和arr[i] 中的最大值
i++;
}
// 如果子节点比父节点大,交换两者的位置,将最大值移动到顶部
if(arr[index] < arr[i]) {
[arr[index], arr[i]] = [arr[i], arr[index]];
index = i;
} else {
break;
}
}
}
console.log(heapSort([5, 10, 2, 15, 1, 12, 6], 4)); // [6, 5, 2, 1]
# 树
JS中树结构一般类似这样
let tree = [
{
id: "1",
title: "节点1",
children: [
{
id: "1-1",
title: "节点1-1"
},
{
id: "1-2",
title: "节点1-2"
}
]
},
{
id: "2",
title: "节点2",
children: [
{
id: "2-1",
title: "节点2-1"
}
]
}
];
# 列表转树
使用对象存储数据,典型的空间换时间
时间复杂度为O(n)、空间复杂度为O(n);
function listToTree(data) {
// 使用对象重新存储数据,空间换时间
let map = {};
// 存储最后结果
let treeData = [];
// 遍历原始数据data,存到map中,id为key,值为数据
for(let i = 0; i < data.length; i++) {
map[data[i].id] = data[i];
}
// 遍历对象
for(let i in map) {
// 根据parentId找到的是父节点
if(map[i].parentId) {
if(!map[map[i].parentId].children) {
map[map[i].parentId].children = [];
}
// 将子节点放到父节点的children中
map[map[i].parentId].children.push(map[i]);
} else {
// parentId找不到对应值,说明是根节点,直接插到跟数组中
treeData.push(map[i])
}
}
return treeData
}
// 测试
let list = [
{ id: 1, title: "child1", parentId: 0 },
{ id: 2, title: "child2", parentId: 0 },
{ id: 6, title: "child2_1", parentId: 2 },
{ id: 4, title: "child1_1", parentId: 1 },
{ id: 5, title: "child1_2", parentId: 1 },
{ id: 3, title: "child3", parentId: 0 },
{ id: 7, title: "child3_1", parentId: 3 }
];
console.log(listToTree(list));
# 深度优先遍历
递归实现,写法简单,时间复杂度为O(n2)
// 递归版本
function deepTree(tree, arr = []) {
if(!tree || !tree.length) return arr;
tree.forEach(data => {
arr.push(data.id);
// 遍历子树
data.children && deepTree(data.children, arr);
})
return arr;
}
// 非递归版本
function deepTree(tree) {
if(!tree || !tree.length) return;
let arr = [];
let stack = [];
// 先将第一层节点放入栈
for(let i = 0, len = tree.length; i < len; i++) {
stack.push(tree[i]);
}
let node;
while(stack.length) {
// 获取当前第一个节点
node = stack.shift();
arr.push(node.id);
// 如果该节点有子节点,继续添加进入栈顶
if(node.children && node.children.length) {
stack = node.children.concat(stack);
}
}
return arr;
}
let tree = [
{
id: "1",
title: "节点1",
children: [
{
id: "1-1",
title: "节点1-1"
},
{
id: "1-2",
title: "节点1-2"
}
]
},
{
id: "2",
title: "节点2",
children: [
{
id: "2-1",
title: "节点2-1"
}
]
}
];
console.log(deepTree(tree)); // ['1', '1-1', '1-2', '2', '2-1']
# 广度优先遍历
思路
- 维护一个队列,队列的初始值为树结构根节点组成的列表,重复执行一下步骤,直到队列为空
- 取出队列中的第一个元素,进行访问相关操作,然后将其后代元素(如果有)全部追加到队列最后
时间复杂度为O(n)、空间复杂度为O(n);
function rangeTree(tree, arr = []) {
let node, list = [...tree];
while((node = list.shift())) {
arr.push(node);
node.children && list.push(...node.children);
}
return arr;
}
let tree = [
{
id: "1",
title: "节点1",
children: [
{
id: "1-1",
title: "节点1-1"
},
{
id: "1-2",
title: "节点1-2"
}
]
},
{
id: "2",
title: "节点2",
children: [
{
id: "2-1",
title: "节点2-1"
}
]
}
];
console.log(rangeTree(tree)); // ['1', '2', '1-1', '1-2', '2-1']
# 查找节点
递归实现,写法简单
function findTreeNode(tree, func) {
for(const data of tree) {
// 条件成立 直接返回
if(func(data)) return data;
if(data.children) {
const res = findTreeNode(data.children, func);
// 结果存在在返回
if(res) return res;
}
}
return null;
}
let tree = [
{
id: "1",
title: "节点1",
children: [
{
id: "1-1",
title: "节点1-1"
},
{
id: "1-2",
title: "节点1-2"
}
]
},
{
id: "2",
title: "节点2",
children: [
{
id: "2-1",
title: "节点2-1"
}
]
}
];
console.log(
findTreeNode(tree, data => {
return data.title === "节点1-1";
})
);
// 打印结果: {id: '1-1', title: '节点1-1'}
# 字符串
# 版本号排序
比如a,b两个版本大小:a为1.rc.2.1,b为1.beta.2
其实rc > beta > alpha
例子 1.2.3 < 1.2.4 < 1.3.0.alpha.1 < 1.3.0.alpha.2 < 1.3.0.beta.1 < 1.3.0.rc.1 < 1.3.0
要求:当 a > b 是返回 1; 当 a = b 是返回 0; 当 a < b 是返回 -1;
思路
- 首先先写一个映射表,建立不同版本的映射关系
- 将不同版本的英文字母,替换成对应的数字,转化为对字符串进行比较
- 字符串比较的原则:取出相同位置的数字进行递归比较
function compareVersion(str1, str2) {
// 创建rc beta alpha,对应的权重值,将版本号转换为纯数字
let map = { rc: 3, beta: 2, alpha:1 };
Object.keys(map).forEach(key => {
str1 = str1.replace(key, map[key]);
str2 = str2.replace(key, map[key]);
})
const arr1 = str1.split('.');
const arr2 = str2.split('.');
function fn(arr1, arr2) {
let i = 0;
while(true) {
// 取出相同位置的数字
const s1 = arr1[i];
const s2 = arr2[i];
i++;
// 若s1 或 s2 不存在,说明相同的位置已比较完成,剩下的位置比较arr1与arr2的长度,长的版本号大
if(s1 === undefined || s2 === undefined) {
return arr1.length - arr2.length;
}
if(s1 === s2) continue;
return s1 - s2;
}
}
return fn(arr1, arr2);
}
// 测试
let str1 = "1.rc.2.1";
let str2 = "1.beta.2";
console.log(compareVersion(str1, str2)); // 1
# 第一个不重复字符的下标
输入一个字符串,找到一个不重复字符的下标
如输入abcabcde,输出6,第一个不重复的字符位d
// 方法一:
// 先使用set去重
// 然后两层遍历,时间复杂度为O(n<sup>2<sup>)
function findAlone(str) {
let arr = str.split('');
// 通过set去重
let aloneArr = [...new Set(arr)];
let val = '';
for(let i = 0; i <= aloneArr.length - 1; i++) {
// 用原始字符串进行遍历 找到唯一的值
if(arr.filter(item => item === aloneArr[i]).length == 1) {
val = aloneArr[i];
break;
}
}
return val ? arr.indexOf(val) ? -1;
}
let str = "abcabcde";
console.log(findAlone(str)); // 6
// 方法二
// 思路:使用map存储每个字符出现的次数
// 该方法时间复杂度与空间复杂度为O(n),从时间上来说,要比第一次方法亏啊
function findAlone1(str) {
if(!str) return -1;
// 使用map存储每个字符出现的次数
let map = {};
let arr = str.split('');
arr.forEach(item => {
let val = map[item];
// val为undefined时,表示未存储,map[item] = 1;否咋map[item] = val + 1;
map[item] = val ? val + 1 : 1;
})
// 一次遍历结果后,在遍历一遍找到出现1次的值
for(let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if(map[arr[i]] === 1) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
console.log(findAlone1(str)); // 6
# 字符串所有排列组合
输入一个字符串,打印出该字符串中字符的所有排列组合
例如输入字符串abc,则打印出由字符a,b,c所能排列出来的所有字符串,结果为:['abc', 'acb', 'bca', 'bac', 'cab', 'cba']
思路
- 利用回溯法(将删除的元素递归后,重新添加到数据中)
- 每次递归,固定开头的字母,比如abc,先固定a,然后交换bc的位置,拿到两个结果abc acb
- 然后交换字符串位置,比如abc递归一轮后,位置变化为bca
- 第二轮,固定b,然后交换ca的位置,拿到两个结果 bca bac
- 同理,依次将字符串中的字符放到头部,并固定,拿到所有情况的结果
/**
* 计算所有字符串的组合
* @param {array} list--字符串列表
* @param {array} result -- 最终结果
* @param {string} current -- 当前的字符串
* @param {string} temp --当前固定的字符
*/
function stringGroup(list = [], result = [], current = '', temp = '') {
current += temp;
if(list.length === 0) {
// 递归的出口,将对应结果添加到list中
return result.push(current);
}
for(let i = 0; i < list.length; i++) {
// 每次递归 固定第一个字符
temp = list.shift();
stringGroup(list, result, current, temp);
// 将删除的temp 重新添加到queue尾部,实现将数组反转的效果,如[a, b,c] 反转为[c, b,c]
list.push(temp);
}
// 这里去重是解决str中有重复的字母,比如str为「aacd」
return [...new Set(result)]
}
console.log(stringGroup('abc'.split('')))
# 字符串是否对称
输入一个字符串,判断是否对称,对称输出true,不对称输出false
输入 abcba; 输出 true
// 方法一:将字符串分为数组,在逆序,在连接为字符串
function isReserveSame(str) {
let temp = str.split('').reverse().join('');
return str === temp;
}
console.log(isReserveSame("abcba")); // true
// 方法二:循环遍历,判断对称位置的字符是否相等
function isReserveSame(s) {
let flat = true;
for(let i = 0; i < parseInt(s.length / 2); i++) {
if(s.charAt(i) !== s.charAt(s.length - 1 - i)) {
flag = false;
}
}
return true;
}
console.log(isReserveSame1("abcba")); // true
# 链表
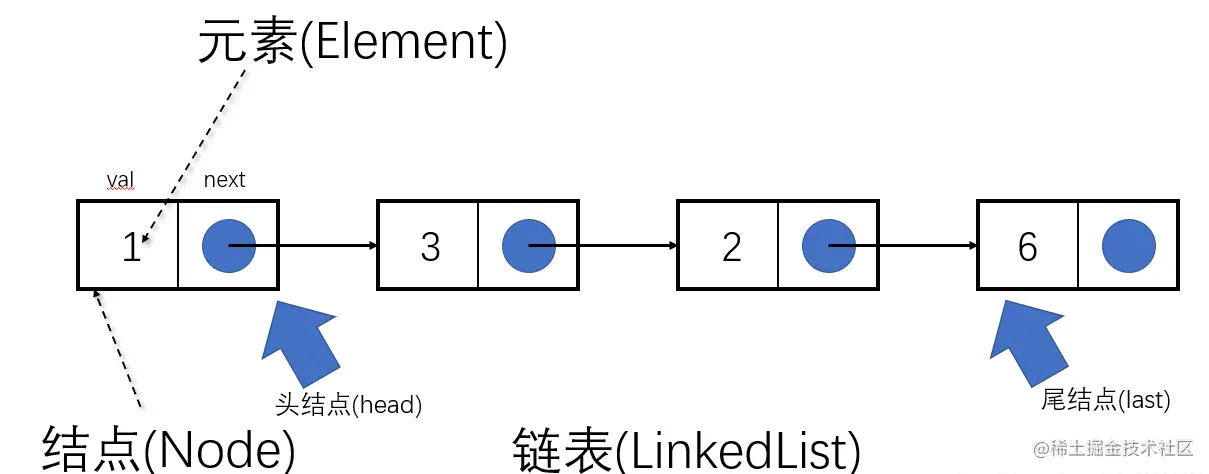
链表:用一组任意存储的单元来存储线性表的数据元素。一个对象存储着本身的值和next(下一个元素)的地址
链表是物理存储单元上非连续的、非顺序的存储结构
链表特点:查询慢,增删快
- 查询慢:链表的地址不是连续的,每次查询都要从头开头
- 增删快:增加/删除一个元素,对链表的整体结构没有影响,所以增删快
链表在开发中也是会用到的数据结构,比如React的Fiber和hook底层都用到了链表
# 创建链表
// 链表Node节点
function Node(data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
// 创建链表
class LinkedList {
constructor() {
this.count = 0; // 链表长度
this.head = null; // 链表开头
}
// 添加节点
push(data) {
let node = new Node(data);
if(!this.head) {
this.head = node;
} else {
let current = this.head;
while(current.next) {
current = current.next;
}
current.next = node;
}
this.count++;
}
// 插入节点
insert(data, index) {
if(index >= 0 && index < this.count) {
let node = new Node(data);
let current = this.head;
if(index === 0) {
// 插到表头
this.head = node;
node.next = current;
} else {
for(let i = 0; i < index - 1; i++) {
// 找到要插入位置的前一个元素
current = current.next;
}
let next = current.next; // 暂存next以后的节点信息
current.next = node;
node.next = next;
}
this.count++;
// 返回插入成功的结果
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
// 按索引值查找
getIndexNode(index) {
if(index >= 0 && index < this.count) {
let current = this.head;
for(let i = 0; i < index; i++) {
current = current.next;
}
return current;
} else {
return null;
}
}
// 按索引值删除节点
removeNode(index) {
if(index >= 0 && index < this.count) {
if(index === 0) {
this.head = this.head.next;
} else {
let current = this.head;
const pre = this.getIndexNode(index - 1);
current = pre.next; // 获取要删除的元素
pre.next = current.next;
}
this.count--;
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
// 查找节点的位置
indexOf(data) {
let current = this.head;
for(let i = 0; i < this.count; i++) {
if(data === current.data) {
return i;
}
current = current.next;
}
}
// 链表转字符串
toString() {
let current = this.head;
let string = `${current.data}`;
// current长度大于1,取下一个节点
if (this.count > 1) current = current.next;
for (let i = 1; i < this.count; i++) {
string = `${string},${current.data}`;
current = current.next;
}
return string;
}
}
// 测试
const link = new LinkedList();
// 增加5个节点
for(let i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
link.push(i);
}
// 索引为1的位置,插入节点6
link.insert(6,1);
// 获取索引2的节点
console.log(link.getIndexNode(2));
// 删除索引3的节点
// console.log(link.removeNode(3));
// 查找位为6的索引
console.log(link.indexOf(6));
// 链表转字符串 1,6,2,4,5
console.log(link.toString());
# 环形链表
链表其中一个节点的next指针,指向另一个节点
创建如上图所示的链表,节点5指向节点3
const link = new LinkedList();
// 增加5个节点
for(let i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
link.push(i);
}
// 创建环形链表,找到值为5的节点,将该节点的next指向值为3的节点
link.getIndexNode(4).next = link.getIndexNode(2)
# 查找环形链表的入口节点
给一个链表,若其中包含环,请找出该链表的环的入口节点,否则,输出null
思路-- 声明两个指针P1,P2
- 判断链表是否有环:P1 P2从头部触发,P1一次走两步,P2一次走一步,如果可以相遇,则环存在
- 从环内某个节点开始计数,在回到此节点时得到链表环的长度length
- P1 P2回到head节点,让P1先走length步,当P1和P2相遇时即为链表环的节点
// 查找环形链表节点
function EntryNodeOfLoop(head) {
if(!head || !head.next) return null;
let p1 = head.next;
let p2 = head.next.next;
// 若p1 === p2 则证明该链表有环
while(p1 !== p2) {
if(p1 === null || p2.next === null) return null;
p1 = p1.next;
p2 = p2.next.next;
}
// 此时p1 是p1、p2重合的点
let temp = p1;
let length = 1;
p1 = p1.next;
// 获取环的长度
while(p1 !== temp) {
p1 = p1.next;
length++;
}
// 找到公共节点
// 此时为什么要将p1 p2重新赋值,因为p2只是重合的点,不一定是入口节点
p1 = p2 = head;
while(length-- > 0) {
p2 = p2.next;
}
while(p1 !== p2) {
p1 = p1.next;
p2 = p2.next;
}
return p1;
}
const link = new LinkedList();
// 增加5个节点
for (let i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
link.push(i);
}
// 创建环形链表,值为5的节点,next指向值为3的节点
link.getIndexNode(4).next = link.getIndexNode(2);
console.log(EntryNodeOfLoop(link.head)); // 打印节点3
# 环中的最后的数字
0,1,..., n - 1这n个数字排成一个圆圈,从数字0开始,每次这个圆圈里删除第m个数字,求出这个圆圈剩下的最后一个数字
约瑟夫环问题

// 使用链表形成一个闭环,最后一个元素的指针指向第一个元素
function findLastNode(n, m) {
if(n < 1 || m < 1) return -1;
const head = {val: 0};
let current = head;
for(let i = 1; i < n; i++) {
// 生成一个链表
current.next = { val: i };
// 将next下一项赋值给current
current = current.next;
}
// 尾部指向头部,形成闭环
current.next = head;
while(current.next != current) {
// 此时current是最后一个节点
for(let i = 0; i < m - 1; i++) {
current = current.next;
}
// 删除第m个节点
current.next = current.next.next;
}
return current.val
}
console.log(findLastNode(5, 3))
# 栈和队列
栈是一种特殊的线性表,仅能在线性表的一段操作,栈顶允许操作,栈底不允许操作
栈的特点是:先进后出,从站定放入元素的操作叫做入栈,取出的元素叫出栈
队列与栈一样,也是一种线性表,不同的是,队列可以在一端添加元素,在另一端取出元素,也就是:先进先出,从一端放入元素的操作成为入队,取出元素为出对
两者区别:栈(先进后出)、队列(先进先出)
# 创建栈和队列
创建栈
// 创建栈 只能从栈尾添加和删除 实现先进后出的效果 class Stack { constructor() { this.arr = []; } // 从栈尾添加 insert(data) { this.arr.push(data); } // 从栈尾删除 del() { return this.arr.pop(); } toString() { return this.arr.toString() } } let stack = new Stack(); stack.insert(1) stack.insert(2) stack.insert(3); stack.del(); console.log(stack.toString()); // 1,2创建队列
// 创建队列 只能从栈尾添加和栈头删除 实现先进先出的效果 class Queue { constructor() { this.arr = []; } insert(data) { this.arr.push(data); } del() { return this.arr.shift(); } toString() { return this.arr.toString(); } } let queue = new Queue(); queue.insert(1); queue.insert(2); queue.insert(3); queue.del(); console.log(queue.toString()); // 2,3
# 栈的入栈和出栈序列
输入两个整数序列,第一个序列arr1表示栈的入栈顺序,请判断第二个序列arr2,是否可能为该栈的出栈序列
思路
- 创建一个栈,模拟入栈、出栈的过程
- id用来记录arr1已出栈的位置
- 当stack栈顶元素和arr2栈顶元素相同时,stack出栈,索引id + 1
- 最终stack栈为空,表示arr1全部元素已出栈
// 判断两个整数序列,第一个序列为入栈顺序,第二序列是否为出栈顺序
function isSameStack(arr, arr1) {
// 创建一个栈,模拟入栈、出栈的过程
let stack = [];
// id用来记录arr1已出栈的位置
let id = 0;
for(let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
// 入栈
stack.push(arr[i]);
// 当stack栈顶元素和arr1栈顶元素相同时候,stack出栈,索引id + 1;
while(stack.length && stack[stack.length - 1] === arr1[id]) {
stack.pop();
id++;
}
}
return stack.length === 0;
}
console.log(isSameStack([1, 2, 3, 4, 5], [2, 4, 5, 3, 1])); // true
# 滑动窗口最大值
如nums = [1,3,-1,-3,5,3,6,7], k = 3,输出结果为[3, 3, 5, 5, 6, 7]
function maxSlidingWindow(nums, k) {
// window存储当前窗口中数据的下标
const window = [];
// result存储窗口中的最大值
const result = [];
for(let i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if(i - window[0] > k - 1) {
// 窗口不断往右移动,当最大值在窗口最左侧,但窗口的长度超出K时的情况,就要把左侧的最大值提出,比如[3,-1, -3],继续往右时,就要把左侧的3剔除
window.shift(); // 剔除窗口长度超出范围时左侧的最大值
}
for(let j = window.length - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
// 当前窗口的值依次和要插入的值做比较,如果小于要插入的值,剔除掉该值,直到window为空为止(保证window中最左侧为最大值)
if(nums[window[j]] <= nums[i]) {
window.pop();
}
}
// 添加右侧新加入的值,传入新值时有两种情况
// 1.新值为最大值时,则window此时为空
// 2.新值不为最大值时,window已剔除掉了比新值小的值
// 始终保证window中最左侧为最大值
window.push(i);
if(i >= k - 1) {
// 窗口从0开始移动,当移动的距离,大于等于目标范围后,以后在往后移动一次,就要写入当前窗口的最大值
result.push(nums[window[0]])
}
}
return result;
}
console.log(maxSlidingWindow([1, 3, -1, -3, 5, 3, 6, 7], 3)); // [3, 3, 5, 5, 6, 7]
# 排序算法
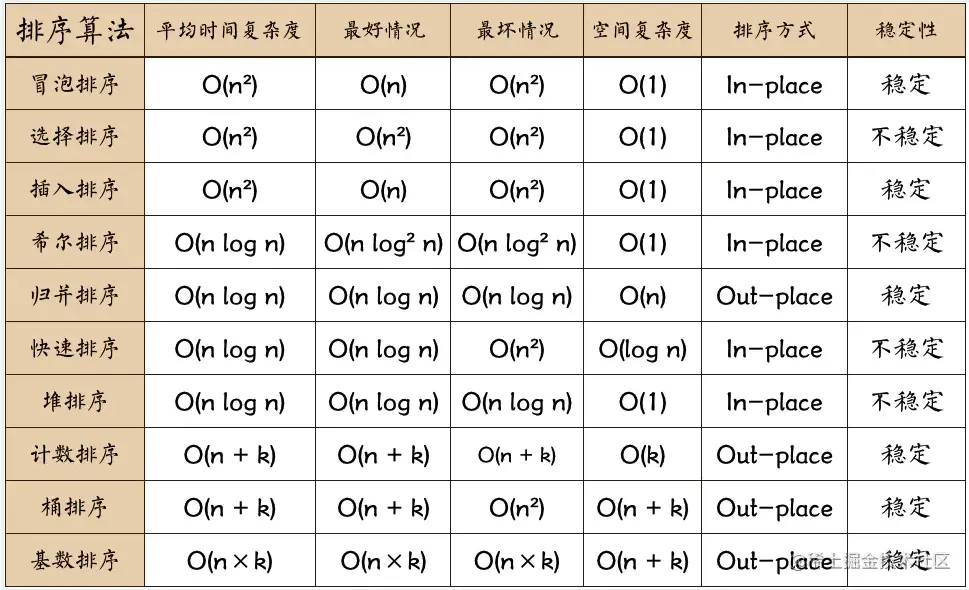
**算法的稳定性:**序列相同元素排序后,先后次序不变及稳定
冒泡排序、归并排序稳定,快速排序、选择排序不稳定
# 冒泡排序
时间复杂度O(n2),稳定
function bubbleSort(arr) {
const length = arr.length;
// 外层循环用控制排序进行多少轮
for(let i = 0; i < length; i++) {
// 内层循环用于每一轮的数据比较
// 注意j的长度范围length - i - 1;
for(let j = 0; j < length - i - 1; j++) {
if(arr[j] > arr[j + 1]) {
[arr[j], arr[j + 1]] = [arr[j + 1], arr[j]];
}
}
}
return arr;
}
console.log(bubbleSort([8, 7, 1, 4, 3])); // [1,3,4,7,8]
# 选择排序
时间复杂度为O(n2),不稳定
思路
从末排序序列中找到最小的元素,放到已排序序列的头部,重复上述步骤,直到所有元素排序完毕
- 外层循环控制进行多少轮
- 内层循环进行数据比较,找到每一轮的最小值
function selectSort(arr) {
// 定义index存储最小值的下标
let index;
// 外层循环用控制排序进行多少轮
for(let i = 0; i < arr.length - 1;i++) {
index = i;
// 内层循环用于每一轮数据比较
// 注意j的起始范围是i + 1;
for(let j = i + 1; j < arr.length; j++) {
// 寻找最小值
if(arr[j] < arr[index]) {
// 保存最小值的下标
index = j;
}
}
// 如果index不是目前的头部元素,则交换两者
if(index !== i) {
[arr[i], arr[index]] = [arr[index], arr[i]];
}
}
return arr;
}
console.log(selectSort([9, 1, 5, 3, 2, 8])); // [1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 9]
# 插入排序
时间复杂度O(n2),稳定
思路
将左侧序列看成一个有序序列,每次将一个数字插入该有序序列
插入时,从有序序列最开始开始比较,若比较的数较大,后移一位。
// 方式一
function insertSort(array) {
// 外层控制循环的次数
for(let i = 1; i < array.length; i++) {
let target = i;
// 内层循环用于每一轮的数据比较
for(let j = i; j >= 0; j--) {
if(array[target] < array[j]) {
[array[target], array[j]] = [array[j], array[target]];
target = j;
} else {
break;
}
}
}
return array;
}
// 方式二
function insertSort(arr) {
// 从第2个元素开始遍历序列
for(let i = 1; j < arr.length;i++) {
let j = i;
// 记录要插入的目标元素
let target = arr[j];
// 从target所在的位置向前遍历,直到找到一个比目标元素小的元素,目标元素插入到该元素之后的位置
while(j > 0 && arr[j - 1] > target) {
// 移动前一个元素的位置,将其向后移动一个位置
arr[j] = arr[j - 1];
j--;
}
arr[j] = target;
}
return arr;
}
# 快速排序
时间复杂度为O(nlogn),不稳定
思路
- 以一个数为基准(中间的数),比基准小的放到左边,比基准大的放到右边
- 再按此方法对这两部分数据分别进行快读排除(递归进行)
- 不能再分后退出递归,并重新将数组合并
// 快速排序
function quickSort(list) {
// 当list.length <= 1时,退出递归
if(list.length <= 1) return list;
// 找到中间点
let mid = Math.floor(list.length / 2);
let base = list.splice(mid, 1)[0];
let left = [];
let right = [];
list.forEach(item => {
if(item > base) {
right.push(item)
} else {
left.push(item);
}
})
return quickSort(left).concat(base, quickSort(right));
}
console.log(quickSort([9, 1, 5, 3, 2, 8]))
# 归并排序
时间复杂度为O(nlogn),稳定
思路
- 将给定的列表分为两半
- 以相同的方式继续划分子数组,直到值剩下单个元素数组
- 以单个元素数组开始,合并子数组,以便对每个合并的子数组进行排序
- 重复第3步单元,直到最后得到一个排好序的数组

function MergeSort(array) {
let len = array.length;
// 当每个子序列中仅有一个1元素时返回
if(len <= 1) return array;
// 将给定的列表分为两半
let num = Math.floor(len / 2);
let left = MergeSort(array.slice(0, num));
let right = MergeSort(array.slice(num, array.length));
return merge(left, right);
function merge(left, right) {
let [l, r] = [0, 0];
let result = [];
while(l < left.length && r < right.length) {
if(left[l] < right[r]) {
result.push(left[l]);
l++;
} else {
result.push(right[r]);
r++;
}
}
result = result.concat(left.slice(l, left.length));
result = result.concat(right.slice(r, right.length));
return result;
}
console.log(MergeSort([6, 5, 3, 1, 8, 7, 2, 4]));
}
# 算法思想
常见的6种算法思想
# 递归
- 优点:使用范围广,简单容易上手
- 缺点: 递归太深,容易发生栈溢出(比如斐波那契数列使用递归进行计算)
- 使用场景:比如树的遍历、快排、深拷贝、查找字符串的所有组合等
# 分治算法
思想:将某问题分成若干个子问题,然后解决多个子问题,将子问题的解合并得到最终结果,
比如快速排序(以中间元素为基准,将原来的数组拆分为左右两个数组,依次类推)
使用场景: 快速排序、二分查找、归并排序
# 贪心算法
最终得到的结果并不一定是整体最优解,可能只是比较好的结果
但是贪心算法在很多问题上还是能够拿到最优解或较优解,所以它的存在还是有意义的
使用场景:买卖股票
# 回溯算法
回溯算法是一种搜索法,试探法,它会在每一步做出选择,一旦发现这个选择无法得到期望结果,就回溯回去
使用场景:比如查找二叉树的路径和二叉树的回溯遍历、字符串中字符的所有排列
# 动态规划
动态规划也是将复杂问题分解成小问题求解的策略,与分治算法不同的是,分治算法要求各子问题是相互独立的,而动态规划各子问题是相互关联的
使用场景: 斐波那契数列和爬楼梯问题(爬楼梯问题的解法和斐波那契数列一样)
# 枚举算法
将问题的所有可能的答案一一列举,然后根据条件判断此答案是否合适,保留合适的,丢弃不合适的
使用场景:长度为n的数组,随机取m个数,有多少种组合
# 算法例子
# 在带权树网络中统计可连接服务器对数目
根枚举
思路和算法
我们可以将每个服务器等价于树中的节点,根据题意可知,如果两个节点a,b和节点c满足以下条件,那么节点 a 和 b是通过c 可连接。
const countPairsOfConnectableServers = function(edges, signalSpeed) {
const n = edges.length - 1;
const graph = Array.from({length: n}, () => []);
for(const [u, v, w] of edges) {
graph[u].push([v, w]);
graph[v].push([u, w]);
}
const dfs = (p, root, curr) => {
let res = 0;
if(curr === 0) {
res++;
}
for(const [v, cost] of graph[p]) {
if(v !== root) {
res += dfs(v, p, (curr + cost) % signalSpeed)
}
}
return res;
}
const res = Array(n).fill(0);
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
let pre = 0;
for (const [v, cost] of graph[i]) {
const cnt = dfs(v, i, cost % signalSpeed);
res[i] += pre * cnt;
pre += cnt;
}
}
return res;
}