# 一面
- leetcode第112题, 路径总和
const hasPathSum = (root, sum) => {
if (root === null) { // 遍历到null节点
return false;
}
if (root.left === null && root.right === null) { // 遍历到叶子节点
return sum - root.val === 0; // 如果满足这个就返回true,否则返回false
}
//不是上面情况,则拆成两个子树的问题,其中一个true就行
return hasPathSum(root.left, sum - root.val) || hasPathSum(root.right, sum - root.val)
}
- 你知道的数组API
| 方法 | 作用 | 是否影响原数组 |
|---|---|---|
| push | 在数组后添加元素,返回长度 | ✅ |
| pop | 删除数组最后一项,返回被删除项 | ✅ |
| shift | 删除数组第一项,返回删除项 | ✅ |
| unshift | 数组开头添加元素,返回长度 | ✅ |
| reverse | 反转数组,返回数组 | ✅ |
| sort | 排序数组,返回数组 | ✅ |
| splice | 截取数组,返回被截取的部分 | ✅ |
| join | 将数组转为字符串,返回字符 | ❌ |
| concat | 连接数组 | ❌ |
| map | 相同规则处理数组项,返回新数组 | ❌ |
| forEach | 遍历数组 | ❌ |
| filter | 过滤数组项,返回符合条件的数组 | ❌ |
| every | 每一项符合规则才返回true | ❌ |
| some | 只要一项符合规则才返回true | ❌ |
| reduce | 接受上一个return和数组下一项 | ❌ |
| flat | 数组扁平化 | ❌ |
| slice | 截取数组,返回被截取区间 | ❌ |
- 实现reduce
Array.prototype.reduce = Array.prototype.reduce || function(fn, initialValue) {
let arr = this;
let base = typeof initialValue === 'undefined' ? arr[0] : initialValue;
let startPoint = typeof initialValue === 'undefined' ? 1 : 0;
arr.slice(startPoint).forEach((val, index) => {
base = fn(base, val, index + startPoint, arr);
})
retrun base;
}
// 第二种实现
Array.prototype.sx_reduce = function(callback, ...args) {
let start = 0, base;
if (args.length) {
base = args[0]
} else {
base = this[0];
start = 1;
}
this.slice(start).forEach((val, index) => {
base = fn(base, val, index + startPoint, this);
})
retrun base;
}
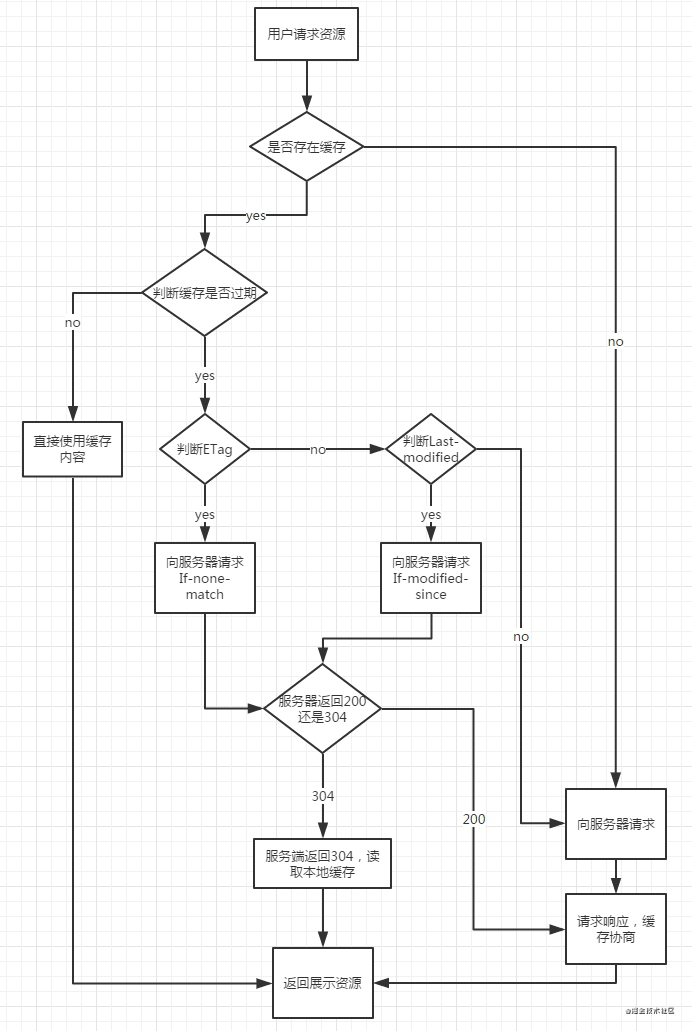
- 将一下HTTP缓存
- vue与react区别和优劣
- vue2 对ts支持较差,vue3已解决
- vue2对jsx支持较差,vue3已解决
- vue和react都是单向数据流
- vue多用模板templeate react多用jsx
- vue和react都用虚拟dom和diff算法
- vue是双向绑定,react是单向绑定
- vue和react都倡导组件化开发
- vue和react都支持服务端渲染
- vue2的状态管理工具是vuex,vue3用pinia,react用redux、mbox、recoil
- vue的diff算法比react更高效
- react的写法更贴近js原生
- hooks、react中class组件和函数组件的区别
- class组件:state和props都是固定地址
- 函数组件:state和props每次都随着渲染更新而更新
- 前端性能优化
- 列表优化:懒加载,虚拟列表,分页
- 重绘重排:合并修改、requestAnimationFrame、will-change
- 提交优化:防抖
- 网络优化:控制并发,取消重复请求,合并请求,http缓存
- webpack优化:代码压缩,gzip,CND,代码分割,合理设置hash,图片转base64
# 二面
- 算法
fn([['a', 'b'], ['n', 'm'], ['0', '1']])
=> ['an0', 'am0', 'an1', 'am1', 'bn0', 'bm0', 'bn1', 'bm0']
解答:
const fn = arr => {
const length = arr.length;
const res = [];
const dfs = (items, str = '', index = 1) => {
if (index > length) {
res.push(str);
} else {
for (const item of items) {
dfs(arr[index], str + item, index + 1);
}
}
}
dfs(arr[0]);
return res;
}
- 手写
u.console('breakfast').setTimeout(3000)
.console('lunch').setTimeout(3000)
.console('dinner')
解答,参考
clas U {
constructor() {
this.tasks = [];
setTimeout(() => {
this.next();
})
}
next() {
const task = this.tasks.shift();
task && task();
}
console(str) {
const task = () => {
console.log(str);
this.next();
}
this.tasks.push(task);
return this;
}
setTimeout(delay) {
const task = () => {
setTimeout(() => {
this.next();
}, delay)
}
this.tasks.push(task);
return this;
}
}
- 事件代理是什么
当子元素都需要绑定相同的事件的时候,这个时候可以把事件直接绑定在父元素上,并通过target对象来判断执行不同的子元素操作,这样可以大大减少绑定事件,减少DOM操作,提高性能
- e.target和e.currentTarget的区别
- e.target:触发事件的元素
- e.currentTarget:事件所绑定的元素
- 写一个事件代理函数,需要判断child是parent的子节点
function proxy(event, cb, parent, child) {
parent[event] = function(e) {
if (parent.contains(child) && e.target === child) {
cb.call(this)
}
}
}
- 看代码说结果
var length = 10;
function fn() {
return this.length + 1;
}
var obj1 = {
length: 5,
test1: function () {
return fn()
}
}
obj1.test2 = fn;
obj1.test1.call() // 11
obj1.test1() // 11
obj1.test2.call() // 11
obj1.test2() // 6
- 从浏览器输入Url到页面渲染发生了什么
- 网络阶段:构建请求行、查询强缓存、DNS解析、建立TCPU连接、发送HTTP请求、响应请求
- 解析阶段:解析html、构建dom树、计算样式、生成布局树
- 渲染阶段:生成图层树、生成绘制列表、生成图块,优先选择视口附近的图块生成位图数据、展示内容
- Tcp和Udp的区别
- 基于连接和无连接
- 对系统资源要求(Tcp较多,UDP少)
- Udp程序结构较简单
- 流模式和数据包模式
- Tcp数据保证正确性,UDP可能丢包
- TCP保证数据顺序,UDP不保证