# 在JS中怎么用:
class Node {
constructor(element) {
this.element = element;
this.next = null;
this.previous = null;
}
}
class LinkedList {
constructor() {
this.header = new Node('header');
// this.head.next = this.header;
}
// find:辅助函数,遍历链表,查找特殊节点
find(element) {
let currNode = this.header;
while (currNode) {
if (currNode.element !== element) {
currNode = currNode.next;
} else {
return currNode;
}
}
return currNode;
}
// insert链表插入节点函数
insert(newElement, hasElement) {
const newNode = new Node(newElement);
const currNode = this.find(hasElement);
newNode.next = currNode.next;
currNode.next = newNode;
}
// findPrevious 辅助函数,寻找待删除节点的前面的那个节点
findPrevious(element) {
let currNode = this.header;
while(!(currNode.next === null) && (currNode.next.element !== element)) {
currNode = currNode.next;
}
return currNode;
}
// remove链表删除节点函数
remove(delElement) {
const prevNode = this.findPrevious(delElement);
if (!(prevNode.next === null)) {
prevNode.next = prevNode.next.next;
}
}
display() {
let currNode = this.header;
while(currNode.next) {
console.log(currNode.next.element);
currNode = currNode.next
}
}
}
const list = new LinkedList();
list.insert('node1', 'header');
list.insert('node2', 'node1');
list.insert('node3', 'node1');
list.insert('node4', 'node3');
list.display()
console.log('----------')
list.remove('node4')
list.display()
// Node {
// element: 'header',
// next: Node { element: 'node1', next: null, previous: null },
// previous: null
// }
使用JavaScript浅谈链表 (opens new window)
# 单向链表
var arr = [1,2,3,4];
var jiao = arr[Symbol.iterator]();
console.log(jiao.next())
手写一个interator
Array.prototype.myInterator = function() {
let i = 0;
let items = this;
return {
next() {
const done = i >= items.length;
const value = done ? undefined : items[i++];
return {
value,
done
}
}
}
}
var jiao = arr.myIterator();
console.log(jiao.next());
# 数据结构
const linkList = {
val: 'a',
next: {
val: 'b',
next: {
val: 'c',
next: {
val: 'd',
next:null
}
}
}
}
# 判断单链表是否带环
//第一种方法
function judge(list) {
var set = new Set();
while(list) {
if (set.has(list)) {
console.log('存在环');
console.log(list);
return true;
}
set.add(list);
list = list.next();
}
return false;
}
//快慢指针,设定快指针fast,慢指针slow,每次循环快指针fast移动两个位置,慢指针移动一个位置
// 若是环形链表快指针总会和慢指针相遇
function judge(head) {
//创建快慢指针
if(head === null) return false
let slow = head, fast = head.next
while(fast && fast.next) {
if (slow === fast) return true
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
}
return false
// 最好用这种--因为下面用到
// if(!head) return false;
// let slow = head, fast = head;
// while(fast) {
// slow = slow.next;
// if(fast.next) {
// fast = fast.next.next;
// } else {
// return false;
// }
// if(slow === fast) return true;
// }
// return false;
}
// 最靠谱吧?
var hasCycle = function(head) {
let traversingNode = head;
while(traversingNode){
if(traversingNode.isVistitd) return true
traversingNode.isVistitd = true
traversingNode = traversingNode.next
}
return false;
};
链表中环的入口节点 剑指 Offer II 022. 链表中环的入口节点 (opens new window)
// 哈希表 -- 时间复杂度O(N) 空间复杂度O(N) var detectCycle = head => { let set = new Set(); let cur = head; while(cur) { if(set.has(cur)) return cur; set.add(cur); cur = cur.next; } return null; } // 快慢指针 时间复杂度O(n) 空间复杂度O(1) var detectCycle = head => { if(!head) return null; let slow = head, fast = head; while(fast) { slow = slow.next; if(fast.next) { fast = fast.next.next; } else { return null; } if(fast === slow) { let ptr = head; while(ptr !== slow) { ptr = ptr.next; slow = slow.next; } return ptr; } } return null; }
# 删除链表中重复的元素
var deleteDuplicates = function(head) {
if (!head) {
return head;
}
let cur = head;
while (cur.next) {
if (cur.val === cur.next.val) {
cur.next = cur.next.next;
} else {
cur = cur.next;
}
}
return head;
};
# 链表的中间结点
// 输入:[1,2,3,4,5]
// 输出:此列表中的结点 3 (序列化形式:[3,4,5])
// 返回的结点值为 3 。 (测评系统对该结点序列化表述是 [3,4,5])。
// 注意,我们返回了一个 ListNode 类型的对象 ans,这样:
// ans.val = 3, ans.next.val = 4, ans.next.next.val = 5, 以及 ans.next.next.next = NULL.
const middleNode = head => {
let slow = head, fast = head;
while(fast && fast.next) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
return slow;
}
# 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点
var removeNthFromEnd = function(head, n) {
let slow = head, fast = head;
// 先让 fast 往后移 n 位
while(n--) {
fast = fast.next;
}
// 如果 n 和 链表中总结点个数相同,即要删除的是链表头结点时,fast 经过上一步已经到外面了
if(!fast) {
return head.next;
}
// 然后 快慢指针 一起往后遍历,当 fast 是链表最后一个结点时,此时 slow 下一个就是要删除的结点
while(fast.next) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
slow.next = slow.next.next;
return head;
};
# 反转链表
给你单链表的头节点head,请你反正链表,并返回反转后的链表
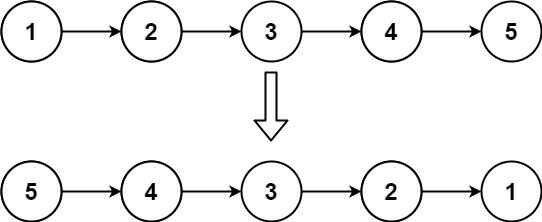
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5]; 输出: [5, 4,3,2,1]
# 迭代
假设链表为 1→2→3→∅,我们想要把它改成 ∅←1←2←3。
在遍历链表时,将当前节点的next指针改为指向前一个节点。由于节点没有引用其前一个节点,因此必须事先存储其前一个节点。在更改引用之前还需要存储后一个节点,最后返回新的头引用
var reverseList = function(head) {
let prev = null;
let curr = head;
while(curr) {
const next = curr.next;
curr.next = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = next;
}
return prev;
}
时间复杂度O(n) 空间复杂度O(1);
# 递归
递归版本稍微复杂一些,其关键在于反向工作
var reverseList = function(head) {
if (head === null || head.next === null) {
return head;
}
const newHead = reverseList(head.next);
head.next.next = head;
head.next = null;
return newHead;
}
时间复杂度O(n) 空间复杂服O(n);空间复杂度主要取决于递归调用的栈空间最多N层
# 合并两个有序链表
将两个升序链表合并为一个新的升序链表并返回。新链表是通过萍姐给定的两个链表所有节点组成的。
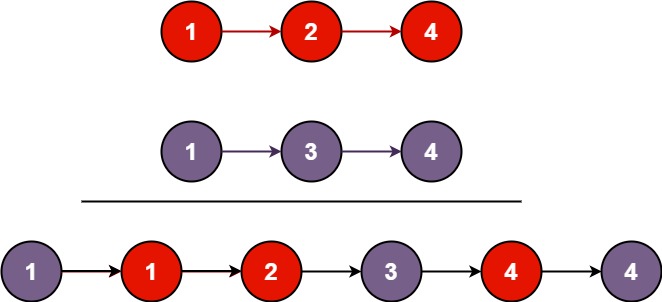
输入:l1 = [1,2,4], l2 = [1,3, 4]
输出 [1,1,2,3,4,5]
# 递归
function mergeTwoLists(l1, l2) {
if (l1 === null) {
return l2
} else if (l2 === null) {
return l1
} else if (l1.val <= l2.val) {
l1.next = mergeTwolist(l1.next, l2);
return l1
} else if (l1.val >= l2.val) {
l2.next = mergeTwolist(l1, l2.next);
return l2
}
}
# 迭代
思路:我们可以用迭代的方法来实现上述算法。当l1和l2都不是空链表时,判断l1和l2哪个链表的投节点的值更小,将较小的节点直接添加到结果里,当一个节点被添加到结果里之后,将对应链表中的节点向后移一位。
var mergeTwoLists = function(l1, l2) {
const prehead = new ListNode(-1);
let prev = prehead;
while(l1 != null && l2 != null) {
if (l1.val <= l2.val) {
prev.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next
} else {
prev.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
prev = prev.next;
}
// 合并后 l1 和 l2 最多只有一个还未被合并完,我们直接将链表末尾指向未合并完的链表即可
prev.next = l1 === null ? l2 : l1;
return prehead.next;
}
# 两数相加
给你两个非空链表来代表两个非负证书。数字最高位位于链表开始位置。他们的每个节点值存储一位数字,将这两数相加会返回一个新的链表
你可以假设除了数字0之外,这两个数字都不会以0开头
示例
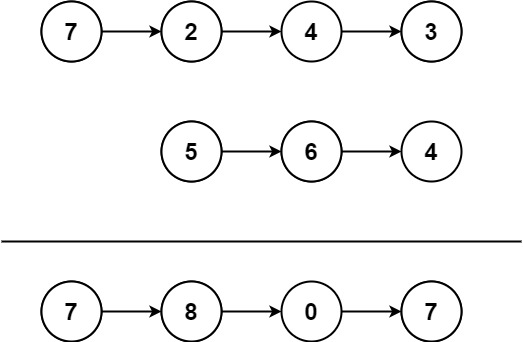
输入: l1 = [7,2,4,3], l2 = [5,6,4]
输出: [7, 8, 0, 7]
输入:l1 = [2,4,3], l2 = [5,6,4]
输出:[8,0,7]
解答:
var addTwoNumbers = function(l1, l2) {
const stack1 = [];
const stack2 = [];
const stack = [];
let cur1 = l1;
let cur2 = l2;
let curried = 0;
while (cur1) {
stack1.push(cur1.val);
cur1 = cur1.next;
}
while (cur2) {
stack2.push(cur2.val);
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
let a = null;
let b = null;
while (stack1.length > 0 || stack2.length > 0) {
a = Number(stack1.pop()) || 0;
b = Number(stack2.pop()) || 0;
stack.push((a + b + curried) % 10);
if (a + b + curried >= 10) {
curried = 1;
} else {
curried = 0;
}
}
if (curried === 1) {
stack.push(1);
}
const dummy = {};
let current = dummy;
while (stack.length > 0) {
current.next = {
val: stack.pop(),
next: null
};
current = current.next;
}
return dummy.next;
};
# 回文链表
const isPalindrome = head => {
if (head === null && head.next === null) return true;
let slow = head;
let fast = head;
let prev = null;
while(fast && fast.next) {
prev = slow;
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
prev.next = null; // 截断为两个链表
// 翻转第二个链表
let head2 = null;
while(slow) {
const next = slow.next;
slow.next = head2;
head2 = slow;
slow = next;
}
// 比较
while(head && head2) {
if (head.val !== head2.val) {
return false;
}
head = head.next;
head2 = head2.next;
}
return true;
}
# 翻转链表二
给你单链表的头指针 head 和两个整数 left 和 right ,其中 left <= right 。请你反转从位置 left 到位置 right 的链表节点,返回 反转后的链表 。
const reverseBetween = (head, left, right) => {
const dummy_node = new ListNode(-1);
dummy_node.next = head;
let pre = dummy_node;
for (let i = 1; i < left; i++) {
pre = pre.next;
}
let cur = pre.next;
for (let i = 0; i < right -left; i++) {
const next = cur.next;
cur.next = next.next;
next.next = pre.next;
pre.next = next;
}
return dummy_node.next
}
# k个一个组翻转链表
给你一个链表,每K个节点一组进行翻转,请你返回翻转后的链表
K是一个正整数,它的值小于或等于链表的长度
如果节点总数不是K的整数倍,那么请将最后的节点保持原有顺序
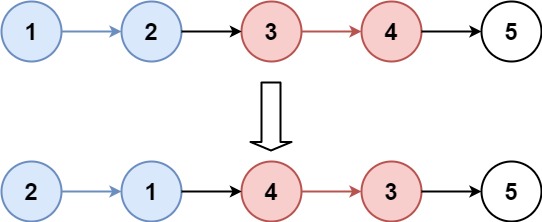
解题
- 分成K个一组,分别翻转
- 在递归中吧翻转后的链表串起来
// 翻转区间[a, b]的元素,注释一是左闭右开
const reverse = (a, b) => {
let prev, cur, nxt;
cur = a;
while(cur != b) {
nxt = cur.next;
cur.next = prev;
prev = cur;
cur = nxt;
}
// 返回翻转后的头结点
return pev;
}
const reverseKGroup = (head, K) => {
if (head === null ) return head;
let a = head, b = head;
for (let i = 0; i < k; i++) {
if (b === null) {
return head;
} else {
b = b.next;
}
}
// 翻转前K个元素
let newHead = reverse(a, b);
a.next = reverseKGroup(b, k);
return newHead;
}
# 排序链表
给你链表的头结点head,请将其按升序排列并返回排序后的链表
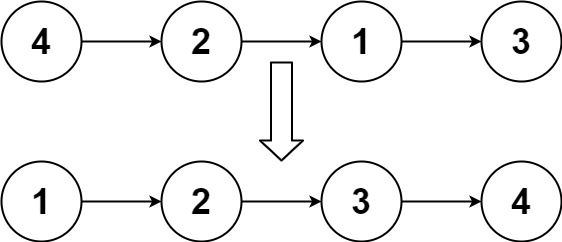
输入:head = [4,2,1,3]
输出:[1,2,3,4]
// 1. 全部切断然后重组
const sortList = head => {
//特判
if(!head) return null;
//全部切断
let s = [];
while (head) {
let t = head.next;
head.next = null;
s.push(head);
head = t;
}
//排序
s.sort((a, b) => (a.val - b.val));
//重组
for(let i = 0; i < s.length - 1; i ++) {
s[i].next = s[i + 1];
}
return s[0];
}
}
// 2.
const sortList = head => {
let cur = head;
let nums = [];
while(cur) {
nums.push(cur.val);
cur = cur.next
}
nums.sort();
const dummy = {};
let current = dummy;
while(nums.length) {
current.next = {
val: nums.shift(),
next: null
}
current = current.next;
}
return dummy.next
}
// 3. 自顶向下归并排序
const merge = (head1, head2) => {
const dummyHead = new ListNode(0);
let temp = dummyHead, temp1 = head1, temp2 = head2;
while(temp1 !== null && temp2 !== null) {
if (temp1.val <= temp2.val) {
temp.next = temp1;
temp1 = temp1.next;
} else {
temp.next = temp2;
temp2 = temp2.next;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
if (temp1 !== null) {
temp.next = temp1;
} else if(temp2 !== null) {
temp.next = temp2;
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
const toSortList = (head, tail) => {
if (head === null) return head;
if (head.next === tail) {
head.next = null;
return head;
}
let slow = head, fast = head;
while(fast !== tail) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
if (fast !== tail) {
fast = fast.next;
}
}
const mid = slow;
return merge(toSortList(head, mid), toSortList(mid, tail));
}
const sortList = head => {
return toSortList(head, null);
}
# 合并k个已排序的链表
function mergeKLists( lists ) {
// write code here
let res = new ListNode(0)
let curr = res
while(true){
let idx = -1
for(index in lists){
if(lists[index] == null) continue
else if(idx == -1) idx = index
else if(lists[index].val < lists[idx].val){
idx = index
}
}
if(idx == -1) break
curr = curr.next = lists[idx]
lists[idx] = lists[idx].next
}
return res.next
}
// 第二种---自顶而下归并 先分在合
const mergeKLists = lists => {
// 当是空数组的情况下
if(!lists.length) return null;
// 合并两个排序链表
const merge = (head1, head2) => {
let dummy = new ListNode(0);
let cur = dummy;
while(head1 && head2) {
if(head1.val < head2.val) {
cur.next = head1;
head1 = head1.next;
} else {
cur.next = head2;
head2 = head2.next;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
// 如果后面还有剩余的就把剩余的接上
cur.next = head1 ? head1 : head2;
return dummy.next;
}
// const mergeLists = (lists, start, end) => {
// if(start + 1 === end) return lists[start];
// // 输入的k个排序链表,可以分成两部分,前K/2个链表和后K/2链表
// // 如果将这前k/2个链表和后K/2链表分别合并成两个排序的链表,再将两个排序的链表合并,那么所有链表都合并了
// let mid = (start + end) >> 1;
// let head1 = mergeLists(lists, start, mid);
// let head2 = mergeLists(lists, mid, end);
// return merge(head1, head2)
// }
// return mergeLists(lists, 0, lists.length);
const mergeLists = lists => {
let len = lists.length;
if(len <= 1) return lists[0];
let mid = len >> 1;
let head1 = mergeLists(lists.slice(0, mid))
let head2 = mergeLists(lists.slice(mid, len))
lists = merge(head1, head2)
return lists;
}
return mergeLists(lists)
}
// 第三种--自低向上合并
var mergeKLists = function (lists) {
if (lists.length <= 1) return lists[0] || null;//当归并的节点只有一个时 返回这个节点
const newLists = [];
//自底而上归并,第一次归并大小为2的链表,第二次归并大小4的链表...
for (let i = 0; i < lists.length; i += 2) {
newLists.push(merge(lists[i], lists[i + 1] || null));
}
return mergeKLists(newLists);
};
const merge = (list_1, list_2) => {//合并两个有序链表
const dummyNode = new ListNode(0);
let p = dummyNode;
while (list_1 && list_2) {
if (list_1.val < list_2.val) {//先将小的节点加入
p.next = list_1;
list_1 = list_1.next;
} else {
p.next = list_2;
list_2 = list_2.next;
}
p = p.next;
}
p.next = list_1 ? list_1 : list_2;//遍历完成还有节点剩余
return dummyNode.next;
};
# 两两交换链表中的节点
给你一个链表,两两交换其中相邻的节点,并返回交换后链表的头节点。你必须在不修改节点内部的值的情况下完成本题(即,只能进行节点交换)。
输入:head = [1,2,3,4]
输出:[2,1,4,3]
var swapPairs = function(head) {
if(!head || !head.next) return head;
let v1 = head,v2 = head.next, v3 = v2.next;
v2.next = v1;
v1.next = swapPairs(v3);
return v2;
};
# 重排链表
给定一个单链表 L 的头节点 head ,单链表 L 表示为
L0 → L1 → … → Ln - 1 → Ln
请将其重新排列后变为:
L0 → Ln → L1 → Ln - 1 → L2 → Ln - 2 → …
不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际的进行节点交换。
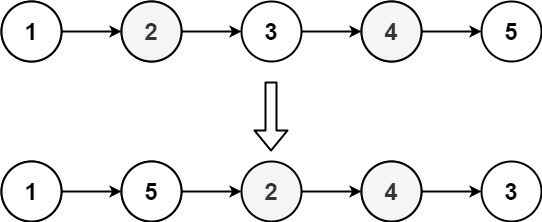
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5]
输出:[1,5,2,4,3]
第一次遍历,构造出双向链表
遍历到最后一个节点之后,反过来拼接,当low和high相遇时,重排结束
var reorderList = function(head) {
const dummy = new Node(0);
dummy.next = head;
// 构造出双向链表
let prev = dummy;
let cur = head;
while (cur !== null) {
cur.prev = prev;
prev = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
// 遍历完之后 prev 在最后一个节点上
let high = prev;
let low = head;
// 奇数个节点 和 偶数个节点 结束的条件不同
while (high !== low && high !== low.next) {
const next = low.next;
low.next = high;
high = high.prev;
low.next.next = next;
low = next;
}
// 断开环
high.next = null;
return dummy.next;
};
// 第二种方法
var reorderList = function(head) {
if(head === null) { return head }
let queue = []
let p = head
while(p) {
queue.push(p)
p = p.next
}
while(queue.length > 2) {
let h = queue.shift()
let t = queue.pop()
t.next = h.next
h.next = t
}
queue[queue.length - 1].next = null
return head
};
← leetcode练习题 二叉树 →