# 前言
可能你会使用vuex状态管理,但是对vuex原理存在着或多或少的疑惑和不解,这篇文章就针对vuex原理进行研究
# Vuex是什么
Vuex是专门为Vue服务,用于管理页面的数据状态、提供统一数据操作的生态系统,相当于数据库mongoDB、mySQL等,任何组件都可以存取存取仓库中的数据。其中vuex类似的还有Redux, Redux大多用于React,针对Redux后续在做补充,现在就让我们好好了解下Vuex到底是啥东西
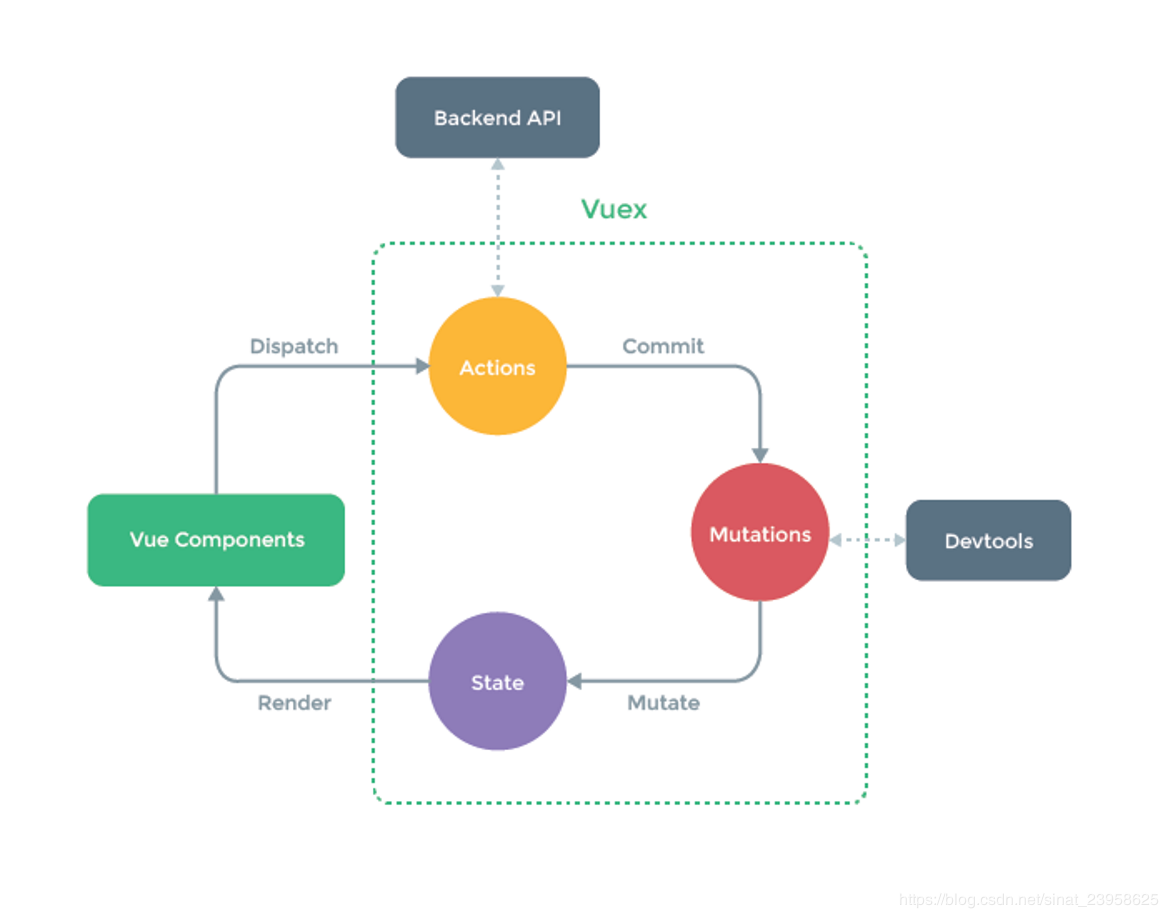
Vuex采用MVC模式中的Model层,规定所有的数据都必须通过action->mutation->state这个流程来改变数据状态的。在结合Vue的数据视图双向绑定实现页面的更新。统一状态管理,可以让复杂的组件交互变得简单清晰,同时在调试时也可以通过DEVtools去查看状态。
在当前前端的spa模块化项目中不可避免的是某些变量需要在全局范围内引用,此时父子组件的传值,子父组件的传值,兄弟组件间的传值成了我们需要解决的问题。虽然vue中提供了props(父传子)、emit(子传父)、兄弟间也可以用localstorage和sessionstorage。但是这种方式在项目开发中带来的问题比解决的问题(难管理、难维护、代码复杂、安全性低)。vuex的诞生也是为了解决这些问题,从而大大提高我们vue项目的开发效率
# 抛出问题
- 使用Vuex只需执行Vue.use(Vuex),并在Vue的配置中传入一个store对象的示例,store是如何实现注入的?
- state内部是如何实现支持模块配置和模块嵌套的?
- 在执行dispatch触发action(commit同理)的时候,只需传入(type, payload),action执行函数中第一个参数store是从哪儿获取的
- 如何区分state是外部直接修改,还是通过mutation方法修改的
# Vue与Vuex的关系
看一下这个vue响应式的例子,vue中的data 、methods、computed,可以实现响应式。
视图通过点击事件,触发methods中的increment方法,可以更改state中count的值,一旦count值发生变化,computed中的函数能够把getCount更新到视图。
<div id="app">
<button @click="increment"></button>
{{getcount}}
</app>
<script>
new Vue({
el: "#app",
// state
data () {
return {
count: 0
}
},
// view
computed: {
getCount(){
return this.count
}
},
// actions
methods: {
increment () {
this.count++
}
},
})
</script>
那么vuex又和vue这个响应时的例子有什么关系呢?
我们可以用vuex实现与vue相同的响应时功能
其实原理是一样的,vuex中也有四个属性值:state、getter、actions、mutations
在没有actions的情况下
- 数据:state -> data。
- 获取数据 getter-> computed
- 更改数据 mutations-> Methods
视图通过点击事件,触发mutations中方法,可以更改state中的数据,一旦state数据发生更改,getters把数据反映到视图
那么actions,可以理解处理异步,而单纯多加的一层。
既然提到了mutions actions这时候 就不得不提commit,dispatch这两个有什么作用呢?
在vue例子中,通过click事件,触发methods中的方法。当存在异步时,而在vuex中需要dispatch来触发actions中的方法,actions中的commit可以触发mutations中的方法。同步,则直接在组件中commit触发vuex中mutations中的方法。
# Vuex实现
下面我们看下vuex中能像vue中实现改变状态,更新视图的功能
Vuex.js
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0
},
//state的值只能通过mutations来修改
mutations: {
increment(state) {
state.count++
}
},
//this.$store.commit("increment")触发mutations中函数"increment"
actions: {
increment({commit}) {
commit("increment"); //this.$store.commit("increment")
}
},
//通过getter中的方法来获取state值
getters: {
getCount(state) {
return state.count
}
}
})
export default store
app.vue
<template>
<div id="app">
<button @click="increment">增加</button>
<!-- 有时候不能直接 强制使用store里面的状态 this.$store.state.count -->
{{this.$store.getters.getCount}}
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
methods: {
increment(){
//this.$store.dispatch("increment")触发actions函数"increment"
this.$store.dispatch("increment")
}
}
}
</script>
# 源码分析
# store注入组件install方法
解答问题:vuex的store是如何注入到组件中的?
首先使用vuex,安装需要插件
Vue.use(Vuex); // vue的插件机制,安装vuex插件
当use(Vuex)时候,会调用vuex中的install方法,装在xuex
下面是install的核心源码
Vue.mixin({
beforeCreate() {
if(this.$options && this.$options.store) {
// 找到根组件main上面挂一个$store
this.$store = this.$options.store;
// console.log(this.$store);
} else {
// 非根组件指向其父组件的$Store
this.$store = this.$parent && this.$parent.$store;
}
}
})
可见,store注入vue的实例组件的方式,是通过vue的mixin机制,借助vue组件的生命周期钩子beforeCreate完成的。即每个vue组件实例化过程中,会在beforeCreate钩子前调用vuexinit方法
解答问题:vuex的state和getters是如何映射到各个组件实例中响应时更新状态呢
# new Vue实现双向数据绑定
this._s = new Vue({
data: {
// 只有data中的数据才是响应式
state: options.state
}
})
# getter实现
// 实现getters原理
let getters = options.getters || {};
// console.log(getters);
// this.getters = getters; // 不是直接挂载到getters上,这样只会拿到整个函数体
this.getters = {};
// console.log(Object.keys(getters)); // ['myAge', 'myName']
Object.keys(getters).forEach(getterName => {
// console.log(getterName);
// 将getterName放到this.getters = {}中
// console.log(this.state)
Object.defineProperty(this.getters, getterName, {
// 当你要获取getterName(myAge)会自动调用get方法
// 箭头函数中没有this
get: () => {
return getters[getterName](this.state)
}
})
})
从上面源码,我们可以看出Vuex的state状态是响应时,是借助vue的data响应式,将state存入vue实例组件的data中;Vuex的getters则是借助vue的计算属性computed实现数据实时监听
# matations实现
let matations = options.matations || {};
// console.log(mutations);
this.mutations = {};
Object.keys(mutations).forEach(mutationName => {
// console.log(mutationName)
this.mutations[mutationName] = payload => {
this.mutations[mutationName](this.state, payload);
}
})
# actions实现
// actions原理
let actions = options.actions || {};
this.actions = {};
forEach(actions, (actionName, value) => {
this.actions[actionsName] = payload => {
value(this, payload)
}
})
# commit dispatch实现
commit(type, payload) {
this.mutations[type](payload)
}
// type是actions的类型
dispatch = (type, payload) => {
this.actions[type](payload)
}
# 原理总结
Vuex是通过全局注入store对象,来实现组件间的状态共享。在大型复杂的项目中(多级组件嵌套),需要实现一个组件更改数据,多个组件自动获取更改后的数据进行业务逻辑处理,这时候使用vuex比较合适。假如只是多个组件间的传递传递数据,使用vuex未免大材小用,其实只用组件间常用的通信方式即可