# 关于hook
# 为什么使用hook
在react类组件(class)写法中,有setState和生命周期对状态进行管理,但是在函数组件中不存在这些,故引入hooks(版本:>=16.8),使开发者在非class的情况下使用更多react特性。
以下是实现一个输入框,类组件和函数组件两种写法的对比:
import React from 'react';
export default class Home extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
name: 'world'
};
}
componentDidMount() {
console.log('组件挂载后要做的操作')
}
componentWillUnmount() {
console.log('组件卸载要做的操作')
}
componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState) {
if (prevState.name !== this.state.name) {
console.log('组件更新后的操作')
}
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<p>hello {this.state.name}</p>
<input type="text" placeholder="input new name"
onChange={(e) => this.setState({ name: e.target.value })}>
</input>
</div>
);
}
}
import React, { useState, useEffect } from 'react';
export default function Home() {
const [name, setName] = useState('world');
return (
<div>
<p>hello {name}</p>
<DemoState />
</div>
)
}
function DemoState() {
const [n1, setN1] = useState(1)
const [n2, setN2] = useState(2)
const [n3, setN3] = useState(3)
useEffect(() => {
setN1(10)
setN1(100)
}, [])
const handleClick = () => {
setN2(20)
setN3(30)
}
console.log('demo-state', n1, n2, n3)
return <button onClick={handleClick}>click</button>
}
上述例子中,useState相当于constructor,完成数据的初始化;
useEffect相当于componentDidMount和componentDidUpdate两个生命周期,通过return () => {}的方式解绑生命周期,相当于componentWillUnmount周期,以监听页面滚动为例,通过effect实现监听与解绑如下:
useEffect(() = >{
window.addEventListener(‘scroll’, throttleFunc)
return () = >{
window.removeEventListener(‘scroll’, throttleFunc)
}
}, [])
在同一个effect钩子中实现绑定与解绑,使状态的管理更加方便、代码更简洁。
此外还有发生在页面渲染前的useMemo相当于shouldComponentUpdate周期等,具体关系如下表:
| class组件 | hooks |
|---|---|
| shouldComponentUpdate | useMemo |
| render | 函数本身 |
| getDerivedStateFromProps | useState 中的 update |
| getDerivedStateFromError | 无 |
| constructor | useState |
| componentWillUnmount | useEffect中的return函数 |
| componentDidUpdate | useEffect |
| componentDidMount | useEffect |
| componentDidCatch | 无 |
结论:使用hooks的函数组件,简化了很多代码,不用维护复杂的生命周期,也不用担心this的指向问题。
# 1.2 什么是hook
hooks挂载在Fiber结点上的memoizedState,filber结构如下:
FiberNode {
memoziedState,
type,
key,
tag,
...
}
memoziedState这个字段很重要,是组件更新的唯一依据。在class组件里,它就是this.state的结构,调用this.setState的时候,其实就是修改了它的数据,数据改变了组件就会重新执行。
也就是说,即使是class组件,也不会主动调用任何生命周期函数,而是在memoziedState改变后,组件重新执行,在执行的过程中才会经过这些周期。
所以,这就解释了函数式组件为什么可以通过hooks改变状态,实际上就是修改了对应fiber节点的memoziedState。
hooks主要有以下特点:
1、无需修改组件结构的情况下复用状态逻辑;
2、可将组件中相互关联的部分拆分成更小的函数,复杂组件将变得更容易理解;
3、每一个组件内的函数(包括事件处理函数,effects,定时器或者api调用等等)会捕获某次渲染中定义的props和state;
4、memo缓存组件 ,useMemo缓存值, useCallback缓存函数;
5、每次render都有自己的props、state和effects。(每一个组件内的函数,包括事件处理函数,effects,定时器或者api调用等等,会捕获某次渲染中定义的props和state);
6、**更新状态的时候(如setCount(count + 1)),React会重新渲染组件,**每一次渲染都能拿到独立的count状态,这个状态值是函数中的一个常量;
7、没有了显性的生命周期,所有渲染后的执行方法都在useEffect里面统一管理;
8、函数式编程,不需要定义constructor、render、class;
9、某一个组件,方法需不需要渲染、重新执行完全取决于开发者,方便管理。
# 1.3 常见hook
useState、useEffect、useMemo、useCallback、useRef、useContext、useReducer…。
所有的钩子都是为函数引入外部功能,react约定,钩子一律使用use前缀命名。
# 常用hook
# 2.1 useState
示例:
const [stateA, setStateA] = useState(0)
参数是初始state(定义初始state最好给出初始值,方便后期维护, 0/false/’’/[]/{})。
返回值:一个是当前state,一个是更新state的函数。
useState的实现很简单,只有两行
export function useState<S>(initialState: (() => S) | S) {
const dispatcher = resolveDispatcher();
return dispatcher.useState(initialState);
}
重点都在dispatcher上,dispatcher通过resolveDispatcher()来获取,这个函数只是将ReactCurrentDispatcher.current的值赋给了dispatcher
function resolveDispatcher() {
const dispatcher = ReactCurrentDispatcher.current;
return dispatcher;
}
useState挂在dispatcher上,resolveDispatcher() 返回的是 ReactCurrentDispatcher.current,所以useState(xxx)等价于ReactCurrentDispatcher.current.useState(xxx)。
useState(hooks)的具体执行过程如下:
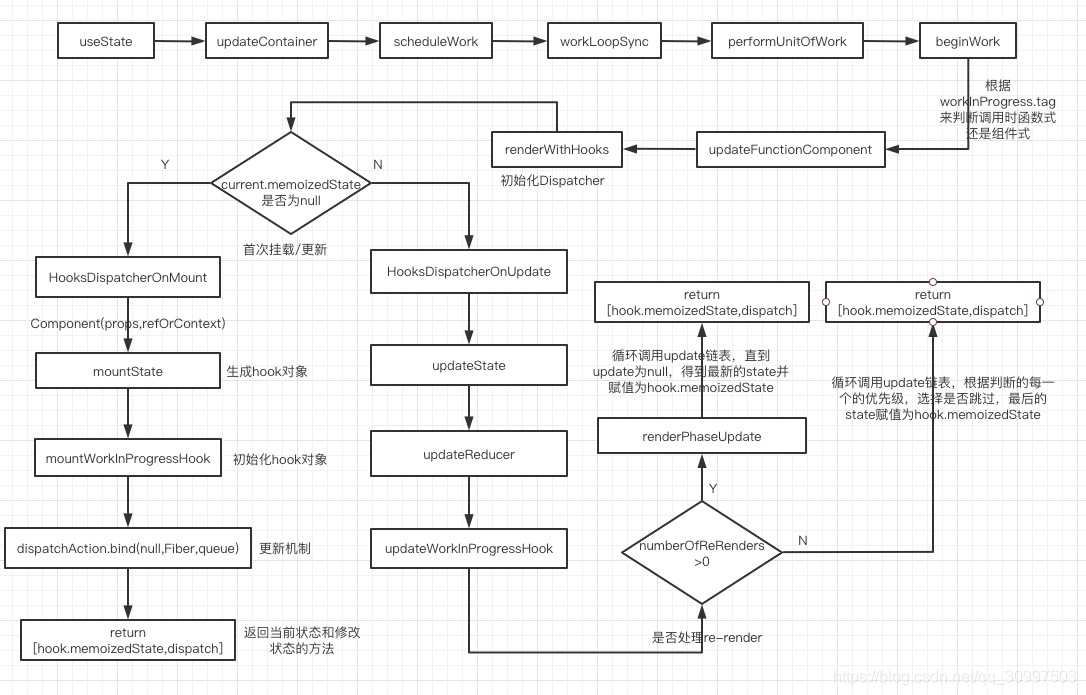
- updateContainer → … → beginWork
- beginWork中会根据当前要执行更新的fiber的tag来判断执行什么,在函数式组件,执行了updateFunctionComponent(判断执行函数式/组件式更新)
首次渲染时,React Fiber 会从 packages/react-reconciler/src/ReactFiberBeginWork.js 中的 beginWork() 开始执行。在beginWork函数中,可以根据workInProgress(是一个Fiber节点)上的tag值来走不通的方法加载或更新组件,如下:
function beginWork(current: Fiber | null, workInProgress: Fiber, renderExpirationTime: ExpirationTime, ) : Fiber | null {
switch (workInProgress.tag) {
case IndeterminateComponent:
{
const elementType = workInProgress.elementType;
return mountIndeterminateComponent(current, workInProgress, elementType, renderExpirationTime, );
}
case FunctionComponent:
{
const Component = workInProgress.type;
const unresolvedProps = workInProgress.pendingProps;
const resolvedProps = workInProgress.elementType === Component ? unresolvedProps: resolveDefaultProps(Component, unresolvedProps);
return updateFunctionComponent(current, workInProgress, Component, resolvedProps, renderExpirationTime, );
}
case ClassComponent:
{
}
}
}
在updateFunctionComponent中,对hooks的处理如下
nextChildren = renderWithHooks( current, workInProgress, Component, nextProps, context, renderExpirationTime, );所以,React Hooks 的渲染核心是renderWithHooks,在renderWithHooks函数中,初始化了Dispatcher。
export function renderWithHooks < Props, SecondArg > (current: Fiber | null, workInProgress: Fiber, Component: (p: Props, arg: SecondArg) = >any, props: Props, secondArg: SecondArg, nextRenderLanes: Lanes, ) : any { ReactCurrentDispatcher.current = current === null || current.memoizedState === null ? HooksDispatcherOnMount : HooksDispatcherOnUpdate; const HooksDispatcherOnMount: Dispatcher = { readContext, useCallback: mountCallback, useContext: readContext, useEffect: mountEffect, useMemo: mountMemo, useState: mountState, }; const HooksDispatcherOnUpdate: Dispatcher = { readContext, useCallback: updateCallback, useContext: readContext, useEffect: updateEffect, useMemo: updateMemo, useRef: updateRef, useState: updateState, }; }在renderWithHooks中,会先根据fiber的memoizedState是否为null,来判断是否已经初始化。因为memoizedState在函数式组件中是存放hooks的。是则mount,否则update(判断是否执行过,没有则挂载,有则更新)
在mount(挂载)时,函数式组件执行,ReactCurrentDispatcher.current为HooksDispatcherOnMount,被调用,会初始化hooks链表、initialState、dispatch函数,并返回。这里就完成了useState的初始化,后续函数式组件继续执行,完成渲染返回。(首次渲染过程)
在update(更新)时,函数式组件执行,ReactCurrentDispatcher.current为HooksDispatcherOnUpdate,被调用,updateWorkInProgressHook用于获取当前work的Hook。然后根据numberOfReRenders 是否大于0来判断是否处理re-render状态:是的话,执行renderPhaseUpdates,获取第一个update,然后循环执行,获取新的state,直到下一个update为null;否的话,获取update链表的第一个update,进行循环,判断update的优先级是否需要更新,对于优先级高的进行更新。(更新过程)
结果返回当前状态和修改状态的方法 以挂载为例,生成一个hook对象(mountState),并对hook对象进行初始化(mountWorkInProgressHook),具体如下: