# 中间件
koa中间件机制:Koa中间件机制就是函数式组合概念Compose的概念,将一组需要顺序执行的函数复合为一个函数,外层函数参数实际上是内层函数的返回值。洋葱模型可以形象的表述这种机制,是源码的精髓和难点
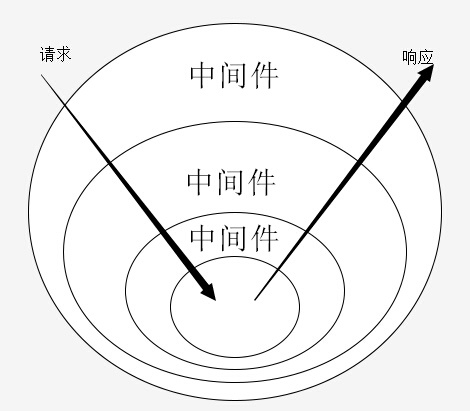
洋葱圈 切面 可以操作 请求前做什么?请求后做什么?
知识储备
const add = (x, y) => x + y;
const square = z => z * z;
const fn = (x, y) => square(add(x, y));
console.log(fn(1,2))
上面就算是两次函数组合调用,我们可以把他合并成一个函数
cosnt compose = (fn1, fn2) => (...args) => fn2(fn1(...args));
const fn = compose(add, square)
多个函数组合:中间件的数目是不固定的,我们可以用数组来模拟
const compose = (...[first, ...other]) => (...args) => {
let ret = frist(...args);
other.forEach(fn => {
ret = fn(ret);
})
return ret;
}
const fn = compose(add, square);
console.log(fn(1,2))
# 异步中间件
上面的函数都是同步的,挨个遍历执行即可,如果是异步的函数呢,是一个promise,我们要支持async + await的中间件,所以我们要等异步结束之后,在执行下一个中间件
function compose(middlewares) {
return function() {
return dispatch(0);
// 执行第0个
function dispatch(i) {
console.log(i)
let fn = middlewares[i];
if (!fn) {
return Promise.resolve();
}
return Promise.resolve(
fn(function next() {
// promise完成后,在执行下一个
return dispatch(i + 1);
})
)
}
}
}
async function fn1(next) {
console.log('fn1');
next();
console.log('end fn1');
}
async function fn2(next) {
console.log('fn2');
next();
console.log('end fn2');
}
function fn3(next) {
console.log('fn3');
}
function delay() {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve();
}, 2000)
})
}
const middlewares = [fn1, fn2, fn3];
const finalfn = compose(middlewares);
finalfn();